Hematology Instruments and Reagents
3-PDAs continue to dominate the hematology market, as of now
Despite a distinct shift toward 5-part differential analyzers, the tried and tested 3-part differential analyzers continue to dominate the market, with an estimated 30,000 units sold globally every year.
Traditional manual methods for characterizing blood cells and components are accepted as being unreliable and time-consuming. Often, re-processing samples and performing additional procedures, such as nucleated red blood cells and optical counting, are necessary to obtain the necessary data for disease detection and monitoring. In addition, as qualified laboratory technicians age, less experienced technologists are replacing them without sufficient training in multiple specializations and complex manual analyses. This makes it challenging to address the labor requirements in multi-discipline laboratories. However, fully automated hematology analyzers can accommodate a wide range of analyses, minimizing manual intervention and human error.
Another significant advantage of utilizing hematology analyzers over traditional cell counting is their large-scale capacity. Hematology analyzers can process hundreds of samples simultaneously, making them ideal for high-throughput industrial, medical, and research applications. Advanced models with improved sensitivity can also detect not just blood cell and platelet count, but also the reticulocyte function and cell size.
Modern hematology analyzers are operated by advanced algorithms that implement data-fusion capabilities to integrate information from multiple separate modules, identify patterns, and detect and correct interfering elements. This function leads to greater convenience in detection and correction of errors, and reduces the need for manual reviews.
Hematology analyzers provide laboratory technicians with access to greater and more specific cell information for highly accurate complete blood count (CBC) with differential and lower review rates. They are crucial for streamlining lab processes and improving diagnostic testing. Like any other industry, hematology analyzers were also impacted by new developments in other areas, such as introduction of laser and efficient pneumatic control, leading to smaller analyzers and increased efficiency.
However, the focus has shifted toward improving clinical utility and exceeding expectations, with new-age data informatics and algorithmic science. Hematology analyzers have evolved greatly, and now they can perform a variety of morphology analyses in addition to cell counting. Aspirations have replaced expectations, and users are interested in achieving even more from hematology analyzers.
Indian market dynamics
The Indian hematology market in 2022 is estimated at ₹1275 crore, a significant increase over 2021. Reagents contributed ₹830 crore, at a 65-percent share, the balance being from instruments. Instruments have seen a miniscule 6-percent increase in 2022 over 2021, by value, thus resulting in an increased percentage contribution of reagents from 60 percent in 2021 to 65 percent in 2022.
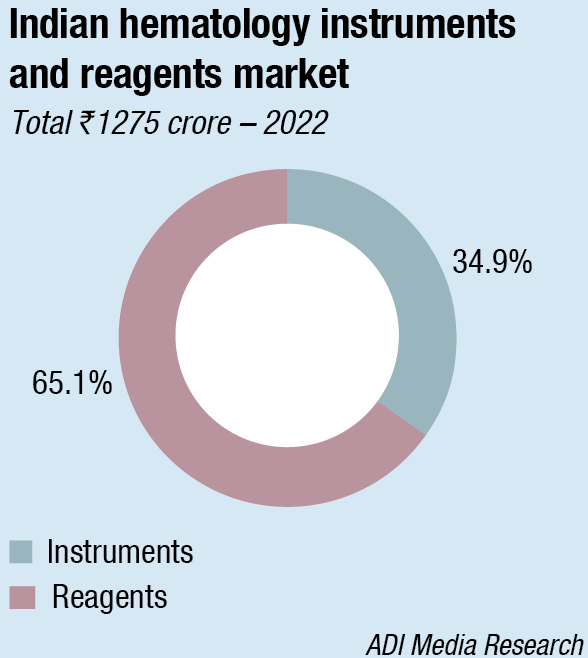
Within the instruments segment, 85 percent of the 5-part high-end analyzers with auto loaders continue to be on rentals. With the price differential between 5-part entry level analyzers and 3-part dual-chamber analyzers narrowing even further, there is a distinct shift toward the 5-part analyzers. Within the 3-part analyzers segment, there are three price points, the discerning large labs, the smaller labs, and the government that in this segment is an exception and prefers the entry-level models. The 3-part single-chamber analyzers segment is a dying category.

With a major consolidation taking place, smaller labs selling out, and the PPP model on the rise, the vendor’s realization is declining. The number of tests is on the rise, but the vendors are having to offer the volume discounts to the large lab that has now taken over the smaller labs.
With the Indian currency nearly 10 percent down against the US dollar in the last one-year, erratic supply chain, and hike in transportation costs, the government’s Make in India program is gaining traction. Vendors are seeking that diagnostics industry also be included in the PLI scheme and the inverted duty structure in imports be resolved.
|
Hematology instruments and reagents market 2022 |
|
| Leading brands | |
| Segment | Brands |
| High-end 5-part instruments | Sysmex, Horiba, Mindray and Transasia |
| Entry 5- part instruments | Sysmex, Horiba, Mindray, Transasia, Boule, Dirui, Urit, Zybio, Bioelad and Genury |
| 3-part instruments | Transasia, Horiba, Mindray, and Sysmex |
| Others – 3 part instruments | Agappe, Beckman Coulter, Vector, Boule, INDO-MIM, Trivitron, Urit, Zybio, Bioelad, Genury, Biogene, Rapid, Meril and many other small importers |
| ADI MEDIA RESEARCH | |
Bar coding is becoming almost mandatory. It not only ensures specimen integrity and prevents fraud, but also helps labs in Tier-II and Tier-III cities and increases the life of the machines. In the US and Europe, major IVD-reagent manufacturers have long since adopted GS1 standards for the unique identification of their products (e.g., Thermo Fisher, Sysmex, BioMérieux, Roche, and others). Yet, some manufacturers are applying GS1 barcodes only at the IVD-reagent’s secondary level of packaging, which limits the granularity of tracing individual items. Using GS1 standards in IVD-reagent distribution in India is gaining momentum. With ongoing adoption by key stakeholders, the overall IVD industry’s distribution costs are reduced while the service quality, security, and customer satisfaction levels increase.
The hematology instruments and reagents market is a rapidly growing segment in the Indian IVD industry. The Covid-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the hematology market in India, with several challenges faced by the industry. However, with the resumption of elective procedures and an increasing focus on healthcare infrastructure, the market is projected to experience significant growth in the coming years.
Automation has been the key to replacing manual workload and countering reduced laboratory throughput, accuracy, and cell-counting speed over time. Hematology analyzers have also decreased in size, thanks to revolutionary advances in computing, electronics and manufacturing, fluidics, and mechanics.
In the upcoming years, the hematology analyzer market in India is expected to expand at a rapid pace. This expansion will be fueled by an increase in the number of cases of blood disorders, automated alternatives for blood testing, greater accessibility, and raised patient awareness following the pandemic. The choice of providers and brands will be based on accuracy, repeatability, trouble-free service, and price.
India’s hematology market dynamics is unique and influenced by several factors. One of the key factors driving the growth is the increasing incidence of blood disorders, such as leukemia, sickle-cell anemia, and thalassemia. With an estimated 1.5 million patients suffering from thalassemia, there is a growing demand for hematology instruments and reagents.
Another factor driving growth is the shift toward automated alternatives for blood testing. With the increasing demand for faster and more accurate testing, automated hematology analyzers are becoming the preferred choice for clinical laboratories. These analyzers are capable of processing large volumes of samples with greater accuracy and speed than manual methods.
Furthermore, accessibility and affordability are crucial factors. As the Indian healthcare system continues to evolve, there is a growing demand for affordable and accessible diagnostic tools. Hematology instruments and reagents that are cost-effective and provide accurate results are highly valued.
In terms of provider and brand choice, accuracy, repeatability, trouble-free service, and price are the key factors that influence the decision-making process. Providers and brands that can deliver these factors are likely to be preferred by customers.
Going forward, the hematology market in India is a rapidly growing segment in the IVD industry, driven by an increase in the number of blood disorders, the shift toward automated alternatives for blood testing, and greater accessibility and affordability. With a projected high CAGR, the market is expected to continue its growth trajectory in the coming years. As the industry continues to evolve, providers and brands that can deliver accurate, reliable, and affordable hematology instruments and reagents are likely to be the preferred choice of customers.
Emerging trends on hematology instruments and reagents
 Thomas John
Thomas John
Managing Director,
Agappe Diagnostics Ltd
The hematology segment contributes about 8–10 percent of India’s IVD market. India’s hematology analyzer market is expected to grow at over 12 percent CAGR in the coming years. Growing incidents of blood disorders, automation options in blood testing and affordability are all contributing to this growth. Precision, efficiency, repeatability, trouble-free service, and affordability determine the selection of suppliers/brands.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI), advanced algorithms, and machine learning to identify abnormalities and provide detailed reports on a wide range of blood parameters, to analyze large amounts of data, as well as the development of portable and handheld devices for POC testing is gathering momentum.
Hematology equipment with built-in connectivity features, connecting to hospital information systems or cloud-based platforms allow seamless data transfer, remote monitoring, and analysis, facilitating collaboration among healthcare professionals.
New-generation hematology types of equipment smartly combine impedance technology with unique algorithms. Machines are compact but throughputs are higher. New-generation machines carry high-tech laser-cut ruby aperture of 70 micron for RBC – platelet and 100 micron for WBC. The system delivers 60 tests/hour and provides 20 parameters along with three histograms that can be viewed on a single screen. For robust and precise operations, the unique fluidic system using proven PTFE syringes is employed.
It is possible through innovative flow cytometry analysis, genomics testing, advanced image processing, microfluidics, usage of multiple scatters, high-speed signal acquisition mechanisms, high-resolution cameras, AI, and machine learning techniques for the accurate morphological view of different cell characteristics.
In place of flow-based counting, a combination platform with digital morphology analysis, cell sorting, and counting is picking up. This will be more helpful in the cancer diagnosis and other blood disorders where cell morphology is a crucial factor. These developments will also reflect in the reagent kits as the focus will shift to more specific stains and dyes, which help in differentiating specific cellular types.
Mispa CountX and Mispa CountX Plus (3-Part), Mispa Count Plus (5-Part), and F 810 (6-Part) are choices from Agappe for highly efficient and affordable hematology diagnostic solutions.
Global market dynamics
The global hematology analyzer market size is estimated at USD 3.59 billion in 2022, projected to hit USD 6.47 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 6.06 percent during 2023–2032. In 2022, the reagents segment generated more than 45 percent of the revenue share, according to Precedence Research.
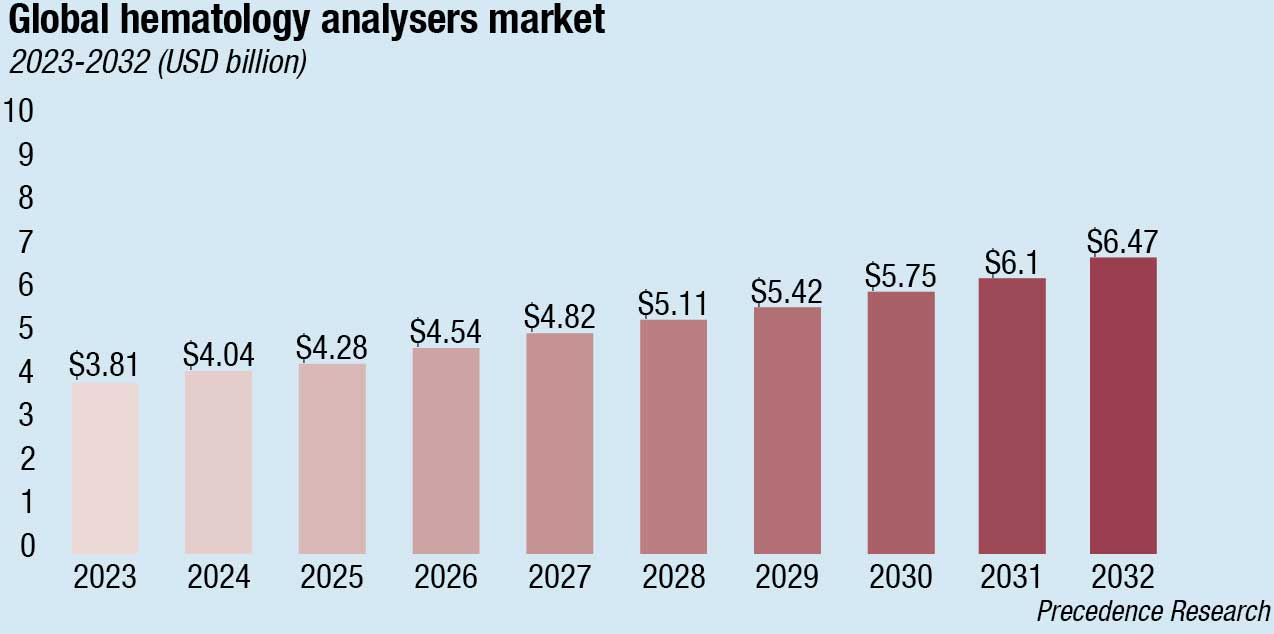
The 3-part differential hematology market is a high-volume segment, with more than 30,000 analyzers sold globally per year. Due to their simplicity, 3-part differential analyzers (PDA) are still cost-efficient devices for developing healthcare systems, while in the more mature markets, the local availability of hemograms is becoming increasingly relevant. For small hospitals, clinics, and physician offices that conduct sophisticated testing, 3-part hematology analyzer system is the best option.
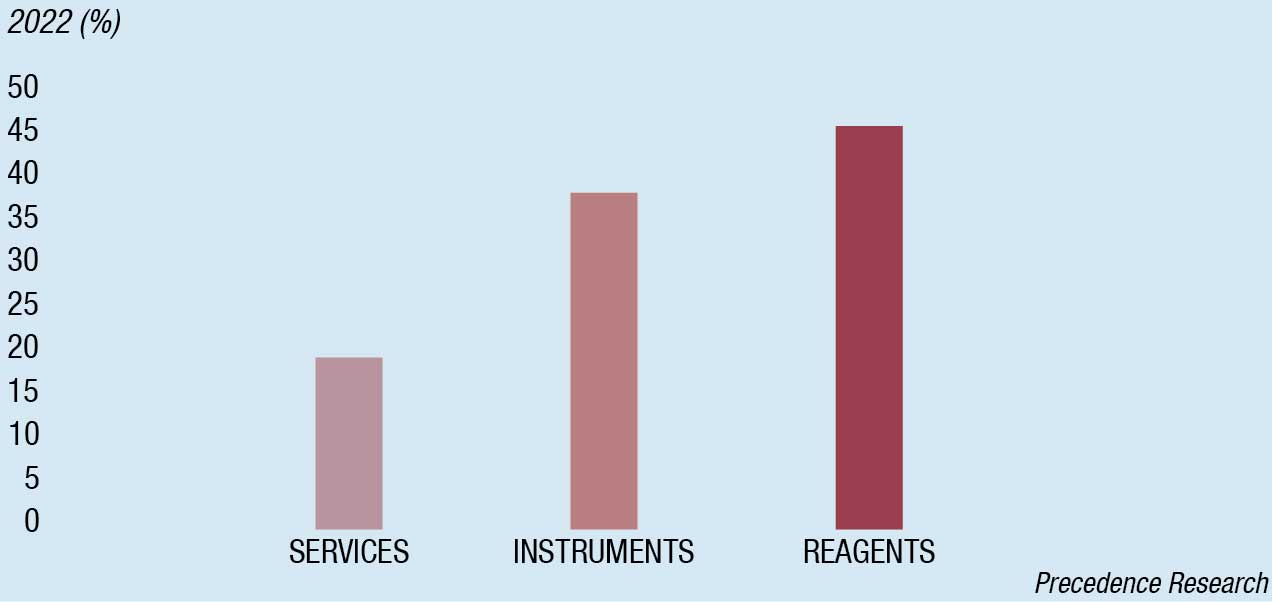
Although 3-part hematology analyzers are more economical for typical hematological tests, 5-part hematology analyzers are gaining in popularity. Additionally, the market is anticipated to rise significantly due to technological developments, the global availability of these instruments, and their reasonable prices.
A new tendency to partially revert the long ongoing trend of centralization in healthcare systems is emerging in various countries, and this has been intensified, if not set off, by the Covid-19 pandemic. Covid exposed the weaknesses of the centralization approach, resulting in initiatives to de-centralize access to diagnostic laboratories by providing local healthcare services in healthcare centers or joint practices that may be connected to a bigger facility, such as a hospital or a private lab in the region.
Technological advancements in Haematology analyzers
 Deepak Valand
Deepak Valand
Product Manager – Hematology,
Transasia Bio-Medicals Ltd.
Haematology analyzers have long been a critical tool in the management of blood related disorders. The recent advancements in technology have led to the integration of slide makers and stainers with haematology instruments, resulting in improved accuracy, efficiency and speed in diagnosis.
Haematology analyzers integrated with slide makers and stainers offer significant advantages over traditional methods. These analyzers automate the process of preparing blood samples and slide staining thus reducing the risk of errors.
Emerging trends
One of the emerging trends in integrated hematology systems is that it offers a range of functions, including cell counting, differential analysis and slide preparation. Advanced technologies such as image analysis and artificial intelligence (AI) help provide faster and more accurate results. The incorporation of user-friendly interfaces make them easier to use and interpret.
Further, with the integration of digital imaging capabilities, these analyzers use digital cameras to capture images of blood cells and thereby identify abnormal cells. This allows for faster and more accurate analysis of blood samples, reducing the time required for diagnosis and treatment.
The integration of slide makers and stainers with haematology analyzers has revolutionized the diagnosis and treatment of blood related disorders.
Advantages of ESR and CBC Combined Instruments
A significant emerging trend is the analysis of CBC and ESR test on a single analyser. ESR is a non-specific indicator of inflammation in the body, and is used to monitor and diagnose a variety of diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and other autoimmune disorders.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms into the CBC data can help to identify patterns and trends in CBC data that may be missed by human observers, potentially improving the accuracy and efficiency of CBC testing.
Modern technological advancements have resulted in significant improvements in healthcare due to advancements in the field of Haematology. The development of CBC with ESR combined instruments and the integration of AI and machine learning algorithms into CBC analysis are just a few examples of exciting innovations that are driving progress in this field.
With advancements of several diagnostic fields, including genetic treatments, pharmacogenomics, bleeding disorders, hemoglobinopathies, stem cell research, and proteomics, the global market for hematology analyzers is predicted to expand significantly in coming years. Likewise, the worldwide hematology market has been expanding due to factors, such as the increase in public awareness and the consolidation of diagnostic laboratory chains.
It is expected that the increasing adoption rates of automated hematology analyzers and the rising consumer demand for high-sensitivity hematological tests will propel the global market over the next 9 years. Additionally, the market has been growing with the rising technological advancements, like the introduction of basic cytometry methods analyzers and the high-throughput expansion of hematology analyzers, and the trend is anticipated to continue over the next few years.
Key market drivers The rising global awareness of chronic diseases is anticipated to fuel the market for hematology analyzers’ revenue growth during 2023–2032. With a high incidence, chronic diseases are the main cause of death. Globally, the rate of these diseases is increasing, spreading to every region of the world, and impacting people from all socioeconomic strata. Healthcare is strongly focused on the early detection and treatment of such disorders to control the progression of such diseases. Previously, only tissue biopsy tests were used for early diagnosis of many chronic diseases, but blood analysis has grown in popularity over a period. The development of the market for hematology analyzers is significantly influenced by improvements in blood indicators for illnesses.
The prevalence of blood disorders is on the rise, technological improvements are accelerating, and automated hematology devices are being adopted at an increasing rate. With several causes and a high fatality rate, blood diseases have emerged as a global health concern. Anemia, blood malignancies, hemorrhagic diseases, and blood-borne infections are just a few of the blood problems that impact millions of individuals annually across all ages.
According to a World Federation of Hemophilia research study published in July 2022, there were a higher number of 1,125,000 males worldwide having an inherited problem of bleeding, and about 418,000 of these have a severe type of condition that is the most underdiagnosed. The Department of Health and Aged Care of the Australian Government reported in 2022 that there were about 330,000 affected babies born every year, 83 percent of whom had disorders of sickle cell and 17 percent had thalassemia, 7 percent of expectant mothers had hemoglobin disorders, and more than 1 percent of the couples worldwide were at risk. Early diagnosis, as well as treatment, are some of the most effective ways to maintain a patient’s quality of life when they have a blood cell problem. The increased prevalence of blood diseases is therefore expected to boost the market in the future.
Key market opportunities In the upcoming years, the use of the product in combination with flow cytometry processes will offer further potential growth prospects for the hematology analyzers market. Moreover, in the hematology analyzers market, many new products are launched in the global market and these new product launches will proliferate the market to a great extent.
Industry updates
The hematology market is fragmented and moderately competitive. Some key industry players include Abbott Laboratories, Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Danaher Corporation (Beckman Coulter), Siemens Healthineers, HORIBA Medical, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. The companies are implementing certain strategic initiatives, such as mergers, new product launches, acquisitions, partnerships, and investments in research and development activities, which help them strengthen their market positions globally.
In July 2022, Beckman Coulter and Scopio Labs partnered to accelerate adoption of hematology digital cell morphology platform. Scopio’s technology employs full-field imaging and AI decision support to truly eliminate manual microscopy, while providing laboratory professionals and clinicians a true workflow benefit. With simple-to-use remote viewing, the Scopio solutions simplify lab operations and improve workflow in a distributed network. High-resolution full-field images can now be shared in real time over a secure hospital network – no more slides being shipped between locations.
In July 2022, HORIBA Medical launched new products in its Yumizen H500 and H550 hematology product family, the compact benchtop hematology analyzers with enhanced performance, new features, and increased benefits.
In June 2022, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. introduced the new EliA RNA Pol III and EliA Rib-P blood tests for aiding in the diagnosis of systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), thus further expanding its comprehensive menu of automated connective tissue disease tests.
In March 2022, Mindray launched novel BC-700 analyzer series, a hematology analyzer series that incorporates both complete blood count (CBC) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) tests. This series, including two open vial models BC-700/BC-720 and two autoloader models BC-760/BC-780, is designed to empower medium-volume laboratories with advanced diagnostic technologies that are applied in the premium products.
In April 2022, Sysmex Europe launched the automated 3-part differential hematology analyzer, XQ-320. The XQ-320 offers superior quality to a range of clinical laboratory situations with robust technology and a new level of usability. It is a dependable device that only needs a small amount of bench space, sample volume, and upkeep in Europe.
Challenges
There are several challenges that the hematology industry faces. One significant challenge is the industry development, which is expected to be constrained by fierce competition among the existing players and the high price of hematology analyzers. Additionally, it is expected that time-consuming and strict regulatory standards for hematological instruments will restrain market expansion in coming years.
The new hematology analyzing devices that are launched in the market are expensive as compared to the already existing analyzers and these automated products have less demand in the underdeveloped and developing nations of the world, and this is another challenge for the growth of the market.
In addition, there is a shortage of qualified laboratory technicians. Many experienced technicians are aging, and the newer technicians replacing them lack sufficient training in multiple specializations and complex manual analyses.
There is a need for consistent quality-control measures to ensure the accuracy and precision of hematology instruments. This requires significant investment in quality-control procedures, training of personnel, and ensuring the consistency and standardization of reagents and controls.
Furthermore, there is a growing demand for faster and more accurate testing, especially in critical care settings. This requires continued research and development of newer technologies and more sophisticated algorithms to achieve greater accuracy and faster turnaround times.
There is also an increasing demand for personalized medicine, which requires tailored treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics. Hematology instruments need to keep pace with this demand by providing more specific and detailed information on individual patient samples.
Finally, with the rise of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, there is a growing need for hematology instruments that can be easily used outside of the laboratory setting, such as in home-based or point-of-care testing. This requires the development of smaller, more portable, and user-friendly instruments that can be used by non-specialists.
Emerging technologies
The increasing worldwide prevalence of hematological disorders and malignancies is exponentially increasing the required amount of diagnostic testing, making the importance of early diagnosis and effective treatment initiation more important than ever. Understanding blood cellular morphology adds to the value of a routine blood count and can help to identify hematologic disorders. Traditionally, peripheral blood smear analysis has been performed manually. To improve both speed and accuracy, however, the industry needs to lean into technology – especially as laboratorians and clinicians are already required to do more with fewer people and resources. Here are some of the trends expected to have an impact on hematology market in coming years:
Technological advancements and emerging trends on hematology analyzers and reagents
 Biju Radhakrishnan
Biju Radhakrishnan
Product Manager – Hematology,
Mindray India
Laboratory diagnosis plays a critical role in healthcare, providing valuable insights for disease detection, monitoring, management, and treatment decisions. In recent years there have been several notable advancements in laboratory diagnosis across various disciplines. The role of laboratories is expanding and an overwhelming rise in testing demands is observed. The big challenge laboratories face today is availability of skilled technologists and specialists.
Hence, laboratories have moved to automation to cater to healthcare needs. The demand from modern era instruments is ease of operation and faster and accurate results, hence relieving laboratory professionals of laborious tasks and empowering pathologists to concentrate on abnormal samples. Advancements have improved accuracy, efficiency, and capabilities of hematology analyzers leading to precise diagnosis and enhanced patient care.
Modern-age hematology analysis has moved from mere counting to morphological analysis. Many hematology analyzers now utilize laser-based flow cytometry technology. Cells pass through a laser beam and measure light, scatter, and fluorescence emitted. Hence providing detailed information of cell size, granularity, and maturity. Along with reliable and accurate WBC differentials’ counting hematology analyzers have improvised technologies for RBC and platelet analysis. Thus, providing utility not only in precise assessment of immune system but also haematopoiesis markers and functioning of bone marrow. Modern age hematology analyzers can process multiple samples simultaneously reducing TAT.
Mindray is dedicated to innovation and pledges to improve haematological findings in coming years to relieve laboratory professionals from cumbersome tasks. Mindray’s new generation hematology analyzers are equipped for all type of laboratory sizes from small to large with its scalable solutions.
Mindray has always empowered laboratories with its innovative technologies. On customer demand to cope up with the recent trends Mindray has developed important parameters like IPF and Optical Platelets without using a separate channel. Hence not only NRBC, IMG but also IPF and Optical Platelet with every CBC-DIFF. Mindray is the first manufacturer to provide ESR result with CBC-DIFF in 90 secs. Mindray has also launched its Automated Digital Morphology System MC-80 last year, which has substantial utility for a high workload laboratory.
Automation. Automated hematology analyzers have revolutionized the field of hematology by providing rapid and accurate blood cell analyses. These instruments can process large numbers of samples quickly and efficiently, reducing the workload of laboratory staff and improving turnaround times for test results. The most advanced automated hematology analyzers can analyze blood cells in great detail, detecting subtle abnormalities that might be missed by manual analysis. These instruments use advanced algorithms to detect abnormalities in blood cells and provide rapid and reliable results.
The hematology analyzers market has seen the emergence of automated solutions from leading manufacturers. The latest automated analyzers are equipped to test components of red blood cells (RBC) and platelets (PLT), while also performing residual white blood cell counting, all in a single sample aspiration. This new capability offers blood-processing centers the potential for significant gains in efficiency, consistency, and accuracy, allowing them to process more samples in a shorter timeframe with minimal errors. These automated analyzers also offer the added advantage of freeing up resources, allowing medical professionals to focus on more critical tasks.
Digitization. Digitization is transforming the way hematology instruments are used and managed. Digital hematology instruments can be connected to hospital information systems, allowing for seamless data transfer and analysis. This improves efficiency and reduces errors in diagnosis. Digital hematology instruments can store patient data and test results in electronic medical records, facilitating longitudinal tracking of patients’ blood disorders.
Integrating POC test results with LIS to support AI-aided diagnostics
 Kristina Rahm
Kristina Rahm
SW Development Manager, Research & Development,
Boule Diagnostics
Where the central laboratory can offer higher throughput and a broader test menu, its extension into testing at point of care supports shorter time to diagnosis that can improve patient outcome. As the panel of available point-of-care (POC) tests evolves, the number of clinical applications that can benefit from a shorter time for medical decision-making is increasing. For example, POC testing is a gamechanger in emergency and critical care. Collaborations between laboratory and healthcare professionals may generate new methods for patient assessments.
IoT and connected medical devices will blur the boundaries between central and satellite testing facilities, and data can be made available for use by various medical stakeholders. Connectivity not only allows monitoring of the performance of devices used outside of the central laboratory. Connectivity also enables communication between the device and the laboratory information system to replace redundant data entry steps, and patient test results and control data can be automatically archived in a central database. If maintained in a proper manner, such databases constitute a rich source of information that can be translated into clinical insights.
EU’s Open Science policy promotes sharing and reuse of research data. As part of the agenda, the FAIR principles for the European Open Science Cloud were set, meaning data should be findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR) to be optimally usable for research.
To support such initiatives, device manufacturers can ensure instruments are connected and that data can be transferred to a central data management system (findable) and stored in a secure yet readily available manner (accessible). Manufacturer and its products should allow coding in a standardized way, for example, using the product’s UDI code from EUDAMED (interoperable), and metadata of importance for the measurement results, such as reagent lot numbers, should be viewable. Generated data should be usable in statistical models together with data from other sources (reusability).
Novel technologies such as AI and machine learning provide the opportunity to assess large amounts of clinical data to reveal patterns otherwise undiscovered. Transferring laboratory clinical data into Big Data brings opportunities for both medical diagnostics and research, ultimately to improve patient care.
Digitization of hematology slides is also transforming cell morphology analysis and changing how scientists work both inside and outside the lab. Because the samples are fully digital, clinicians and lab professionals have the ability to analyze samples from anywhere in their hospital’s secure network, supporting more collaboration and faster review.
Miniaturization. The miniaturization of hematology instruments has not only enabled the development of smaller and more portable devices but it has also revolutionized the field of healthcare. These smaller devices can now be used in remote or underserved areas, where access to laboratory infrastructure is limited, allowing for better healthcare delivery to those in need.
Portable hematology instruments have made point-of-care testing a reality, allowing for faster diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders. This is particularly useful in emergency situations, where time is of the essence, and quick and accurate diagnoses can be the difference between life and death.
In addition to providing faster results, these portable devices are also more user-friendly and require less training than traditional laboratory equipment. This means that healthcare providers with minimal training can use these instruments to perform hematology tests, expanding access to high-quality care to a larger population.
Overall, the miniaturization of hematology instruments and the development of smaller and more portable devices have had a profound impact on the field of healthcare. They have enabled faster and more accurate diagnoses, expanded access to high-quality care, and improved health outcomes for patients in remote or underserved areas.
Artificial intelligence and 3D printing technology. The introduction of AI and 3D printing technology has had a significant impact on the field of hematology analysis. These technologies have enabled the development of new and advanced hematology instruments that are more accurate, efficient, and versatile.
Keeping pace with time to provide a wide variety of customized solutions
 Nitin Srivastava
Nitin Srivastava
Vice President (Sales & Marketing),
Vector Biotek Pvt. Ltd. (A Beacon Group Company)
Hematology refers to the branch of medical science, which incorporates study of blood, its diseases, treatments, and malignancies including hemophilia, blood clots, leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma, sickle cell anemia, and likewise. Amongst the hematology procedures, blood count is categorized as the most common test.
The global hematology market is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 8.2 percent during the period 2023 to 2028, and it is expected to reach from USD 9.12 billion in 2023 to USD 13.52 billion in 2028. The occurrence of pandemic has had a positive impact on hematology market due to the frequent need for examining patient blood, using hematology analyzer to test and monitor the disease. Specific tests following neutrophilia, leukocytosis, lymphopenia, and thrombocytopenia played a significant role in findings in patients with SARS Cov2 infection, thus making it a standard procedure, and thereby providing market growth opportunity.
Hematology analyzers widely used now incorporate technological solutions in order to recognize cell types in a blood sample and to count them individually to generate a complete blood count, including WBC differential. In addition to these primary functions of cell counts and differential leukocyte analysis, these analyzers are capable of reporting many additional parameters and can provide much more information than what they are intended to provide but, unfortunately, they are not being optimally utilized to their potential. The new information available with these additional parameters may help the clinician in the screening and diagnosis of many disease states.
The modern-day analyzers are providing five to seven parts differential white‑cell analysis, based on different technologies, such as electrical impedance, radiofrequency conductivity, light scatter, fluorescent scatter, cytochemistry, etc. In addition to this, they also provide additional information in the form of cell population data (CPD), lymph index, granularity index, large unstained cell population, and hemoparasites, which can be used for screening of benign and malignant hematological conditions.
Beacon Group has made consistent efforts starting from the millennium, and keeps pace with time to provide a wide variety of customized solutions for hematology instrumentation and allied reagents, making Beacon brand a leading solution provider in the hematology business segment.
One of the most significant changes in hematology analysis has been the shift toward cell sorting and counting, which is becoming increasingly popular overflow-based counting. Cell sorting and counting involves separating individual cells from a mixture and analyzing them individually. This method allows for more precise analysis of individual cells, resulting in more accurate diagnoses of blood disorders.
In addition, the combination with digital morphology has emerged as a powerful tool in the diagnosis of blood diseases and cancer. This platform combines traditional hematology methods with digital image analysis and AI algorithms to provide more detailed and accurate diagnostic information. The digital morphology platform allows for the analysis of individual cells at high resolution, identifying subtle abnormalities that may not be detectable with traditional methods.
AI is increasingly being integrated into hematology instruments to improve accuracy and speed of analysis. AI algorithms can analyze large datasets of blood cell images and detect patterns that may be difficult for human analysts to identify.
By using AI, hematology instruments can provide more precise diagnoses, allowing for more targeted treatment and better patient outcomes.
3D printing technology has also been used to develop new hematology instruments, such as microfluidic devices that can sort and analyze individual blood cells. These devices are more efficient and versatile than traditional methods, allowing for more precise analysis of individual cells and more accurate diagnoses of blood disorders.
The introduction of AI and 3D printing technology has enabled significant advancements in the field of hematology analysis. These technologies have facilitated the development of new and advanced hematology instruments, leading to more accurate and efficient diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders.
Technological recursion, 3-part hematology analyzers
 John Mathayi
John Mathayi
Head of Business Development and Marketing,
Indo-Medx
The increasing outbreaks, mutations, emerging pathogens, and growing resistance place pressures on healthcare systems. Blood disease is the most dangerous disease that infects millions of people around the world, so it is important to diagnose and monitor its prognosis, treatment, and prevention.
To diagnose such diseases, hematology analyzers are being used predominantly by quantitative and qualitative analyses of cell counts and additional information such as cell population data and lymph index.
As other medical technologies, the 3-part hematology analyzer has to adapt to current changes in healthcare, including advancements in technology such as:
Improved technology. The latest 3-part hematology analyzers incorporate advanced technology, such as improved optics and sophisticated algorithms, to provide more accurate and reliable results. Some analyzers also include automated sample preparation and handling systems, which reduce the risk of errors and improve turnaround times.
Point-of-care testing. Point-of-care (POC) testing is becoming increasingly popular, particularly in resource-limited settings or where immediate test results are required. Some 3-part hematology analyzers are now available as POC devices, allowing to perform CBCs at the patient’s bedside or in the field.
Customization of test panels. Depending on the specific needs of a patient or healthcare facility, some can be customized to include additional parameters, such as reticulocyte counts or advanced WBC differentials such as NLR, LMR, and PLR. They function as novel biomarkers of systemic inflammation, which are closely related to immune response.
Brief about test panels. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an independent risk factor for Covid-19 and has been suggested to be associated with cardiac arrhythmia, inflammatory bowel disease, thyroiditis, malignant nodules. They are also associated with a variety of other diseases. Platelet-to- lymphocyte ratio (PLR) has been suggested to be associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus and bowel disease it can also be prognostic marker of fibrosis in patients. Therefore, these markers have been widely used in clinical practice.
Introducing CELLOMAX the 3-part hematology analyzer that has transformed the field of hematology analysis, empowering healthcare professionals with faster, more accurate, and comprehensive blood test results with additional parameters such as NLR, PLR, P-LCC, & P-LCR.
Point-of-care testing. Point-of-care testing for hematology is expanding in many areas of the world where it provides real benefits in managing patients’ needs quickly and efficiently. There have been several important areas in the development of point-of-care full blood count testing analyzers. They have become easier to use and more reliable. This is accomplished by robust design and user-friendly software development, which means that they can be safely operated by non-laboratory personnel, and inspire confidence in the results.
Monocyte distribution width (MDW) and its role in the early detection of sepsis
 Karan Bhatia
Karan Bhatia
Head – Marketing (South West Asia),
Beckman Coulter Diagnostics
Monocyte distribution width (MDW) is an in vitro diagnostic parameter that reflects a change in the volume of circulating monocytes in response to pro-inflammatory signals from infectious organisms – referred to as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
Intended use of MDW
MDW is the only USFDA-cleared hematological biomarker that helps to establish severity of infection and risk of sepsis in adult patients in the emergency department. It is available on the Beckman Coulter DxH 900, and intended for use with adult patients presenting to the emergency department, on whom a white cell differential test has been ordered; however, MDW should not be used as the sole basis to determine the absence of sepsis.
Measurement of MDW
When there is an infection or inflammatory process in the body, the bone marrow releases more WBCs into the blood. Monocytes and neutrophils represent the first-line response during an infection. The accompanying inflammatory process may result in their activation, and ultimately morphological and functional changes, which are detected by the proprietary near-native state characterization capability.
Significance of MDW for clinicians
There is a large unmet clinical need for the early detection of sepsis in patients with or developing sepsis. The detection of sepsis is frequently delayed, which can lead to delay in treatment. Earlier administration of sepsis-specific treatments, particularly antibiotics, is associated with improved clinical outcomes, including significantly reduced mortality. Lack of sepsis recognition is one of the common causes of its misdiagnosis, contributing to adverse outcomes due to delays in definitive antimicrobial treatments.
Existing biomarkers of sepsis, such as procalcitonin and lactate are typically ordered only if the clinician already has a high index of clinical suspicion of sepsis. Most critical unmet needs are the identification and alert of sepsis, and the discrimination of sepsis from systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). MDW has been studied for the past decade with more than 16 peer-review publications and over 21,000+ patients, confirming the robustness and reproducibility of MDW performance in different patient populations.
These devices can be used outside of a laboratory setting and provide rapid results, enabling faster diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders. They are particularly useful in remote or resource-limited settings, where access to laboratory infrastructure is limited.
Overall, technological advance- ments in hematology instruments are improving accuracy, speed, and efficiency in the diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders. These trends are expected to continue to shape the industry in the coming years.
Digital microscopy and artificial intelligence – Are we in control of our own future?
 Dr Sonal Jain DM (hematopathology)
Dr Sonal Jain DM (hematopathology)
Senior Consultant (CDC projects),
Art of Healing Cancer
Digital health was considered only hype before the pandemic struck the world in 2019. During the pandemic, digital health was the only hope. Now, it is moving toward healing. Digital health is now the default operating system of healthcare.
People are now more accustomed to digital tools, be it retail, banking, government, or communications, and the same is expected in healthcare too. The distribution of doctors remains an enormous challenge with specialist doctors and services skewed in favor of metropolitan cities. This puts a stress on the healthcare system, making it more difficult to get early diagnosis and consequent treatment.
Also, chronic diseases require continuous patient engagement to manage their condition, which cannot be done without technology integration.
The laboratory services are always in forefront when it comes to adopting new technology.
Artificial Intelligence has the potential to revolutionize laboratory services. Artificial Intelligence is helping automate laboratory workflows, from sample processing to data analysis and reporting. This is helping to reduce errors, increase efficiency, and free up laboratory staff to focus on more complex tasks.
Artificial Intelligence algorithms are being used for predictive analysis. It can analyze large datasets to identify patterns and predict outcomes, or identifying the most effective treatment options for a particular condition.
Artificial Intelligence is particularly helpful in big data analysis. AI can analyze large volumes of laboratory data to identify patterns and trends that may be difficult to detect manually. This can inform research and clinical decision making.
Digital microscopy, assisted by image analysis, is increasingly finding its place in the pathology laboratories. AI-powered image analysis algorithms can quickly analyze microscope images to help identify cells, bacteria, and other microorganisms. This can significantly reduce the time and effort required to manually identify and classify samples.
AI algorithms can automatically detect and classify cells, tissues, and other structures in pathology images, leading to more accurate and efficient diagnoses. AI algorithms can quantify the features of pathology images, such as the size, shape, and texture of cells and tissues. This can help identify subtle changes that may be missed by human observers.
Artificial Intelligence can help predict patient outcomes, based on pathology image analysis, such as the likelihood of disease progression or response to treatment. The process requires digitization of the microscopic slide, using slide scanners followed by image analysis software (with or without remote reporting software).
Slide scanners are specialized devices that allow high-resolution digital scanning of glass slides, containing tissue samples or stained smears (peripheral smears, bone marrow aspirate smears). These scanners are used to create digital images of microscopic slides, which can be then viewed, processed, and analyzed, using computer software.
Some popular slide scanners for histopathology are Leica Biosystems, Hamamatsu NanoZoomer S60, 3.3DHISTECH Pannoramic 250 Flash III, Roche Diagnostics, Olympus VS120, etc.
Some popular slide scanners for hematology slides are Sysmex hematology slide scanner, DigiPath Pro, CellaVision, SigTuple AI100, Siemens ADVIA 2120i, and many more. Some image analysis software commonly used in healthcare and research are ImageJ, CellProfiler, QuPath, HALO, Visiopharm, etc.
The choice of software often depends on the specific application and the type of data being analyzed.
This process facilitates remote consultation and improve the accuracy and consistency of diagnoses and possible collaborations.
Digital and telereporting tools are here to stay and evolve. These tools can be instrumental in looking after medical deserts. If used judiciously, these can be instrumental in equitable healthcare for all.
However, it is important for pathologists to work closely with Artificial intelligence developers to ensure that the algorithms are validated, reliable, and transparent.
Additionally, it is important to consider the ethical implications of Artificial Intelligence’s role in healthcare, especially in terms of patient privacy and consent. To be in control of our own future, we should accept it and be party to its development.
Outlook
The increasing prevalence of hematological disorders and malignancies has made early diagnosis and effective treatment initiation more critical than ever. To meet this challenge, the hematology industry has turned to technology, and various trends are expected to have an impact on the hematology market. These trends include automation, digitization, miniaturization, AI, 3D printing, and point-of-care testing. These advancements have enabled the development of new and advanced hematology instruments that are more accurate, efficient, and versatile than ever before, leading to more precise diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders, improved health outcomes, and expanded access to high-quality care. The way forward for the industry is to continue to embrace technology and innovation to meet the growing demand for hematological diagnosis and treatment.
DHematology in India – A current overview
 Dr (Prof) Rakesh Chopra
Dr (Prof) Rakesh Chopra
Former Chairman and Head Medical Oncology/Hematology/BMT
Hematology, the study of blood and blood disorders, has emerged as a significant discipline. Over the past few decades, India has made significant strides in hematology. The Indian Society of Hematology & Blood Transfusion (ISHBT), established in 1956, has been instrumental in advancing the field. There are also specialized hematology departments in major medical institutions across the country, contributing to patient care, research, and medical education.
Several Indian hospitals now offer advanced diagnostic and treatment options, including bone marrow transplantation and immunotherapy. There has also been an increase in clinical trials in India.
However, there are substantial challenges that need addressing. One of the significant issues is the uneven distribution of resources. While metropolitan cities have seen substantial progress, rural areas remain under-resourced. The lack of trained hematologists and adequate diagnostic facilities in these regions often result in delayed or misdiagnosis of hematological disorders.
Access to affordable treatment is another pressing issue. Advanced treatments, such as bone marrow transplants or targeted therapies for blood cancers, are often prohibitively expensive for the average Indian citizen. Moreover, the coverage of these treatments under the public health insurance schemes is limited.
To tackle these issues, a multi-pronged strategy is necessary. Strengthening public health infrastructure, expanding health insurance schemes to include advanced hematological treatments, and promoting telemedicine for reaching remote areas are some of the measures needed.
Educational initiatives are also crucial. Medical colleges must emphasize hematology in their curricula, and more postgraduate and fellowship programs in hematology should be established.
In terms of research, India’s diverse genetic pool presents a unique opportunity for studying various hematological disorders. More funding and policy support are needed to harness this potential and contribute to global scientific knowledge.
In conclusion, hematology in India has come a long way but still has significant challenges to overcome. With strategic planning, investment in healthcare infrastructure, and focus on education & research, India can effectively address the burden of hematological disorders and become a global leader in this field.












