Devices & Utilities
Bridging the gap
COVID-19 outbreak may be the right impetus for lawmakers and regulatory agencies to promulgate further measures that facilitate more widespread adoption of telemedicine.
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought telemedicine into a new light. As medical professionals need to stay healthy and disease-free, the need for remote technologies has skyrocketed.
Telehealth is bridging the gap among people, physicians, and health systems, enabling everyone, especially symptomatic patients, to stay at home and communicate with physicians through virtual channels, helping to reduce the spread of the virus to mass populations and the medical staff on the frontlines.
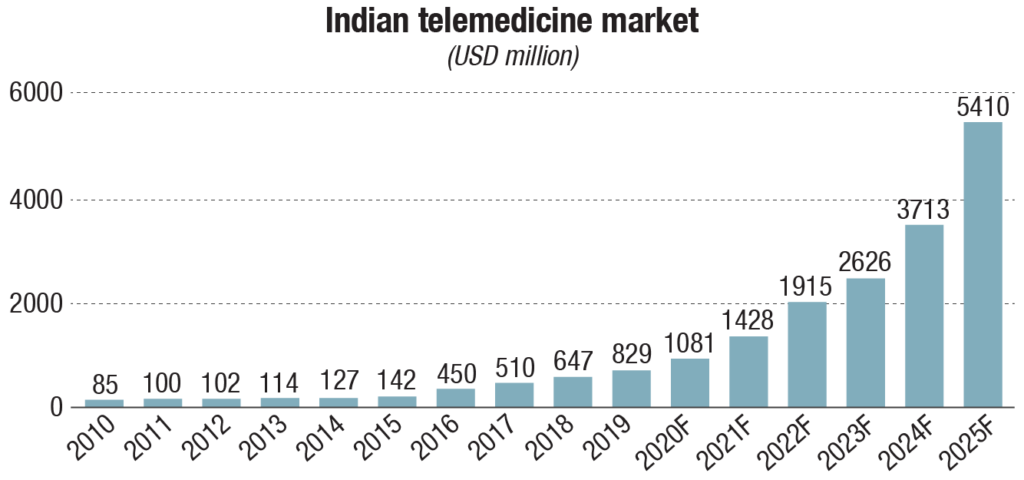
Telemedicine activities in India were started in 1999. The Indian Space Research Organization has been deploying a SATCOM-based telemedicine network across the country since that year. However, the reality is that only a handful of people have adopted the concept. It is only in 2020 that the ongoing COVID-19 crisis is forcing healthcare institutions and regulatory bodies to turn to alternative ways of providing healthcare while limiting exposure to the virus.
And telemedicine is presenting itself as the ideal solution to these woes by limiting patient displacement to hospitals, allocating hospital capacity to important cases, all while curbing the disease’s spread. Telemedicine will reduce the time of consultations and improve the quality of healthcare services in rural areas too, removing many of the infrastructural challenges.
The powers that be are advocating for telemedicine to monitor patients and reduce risks of them spreading the virus by traveling to hospitals. Various government agencies, the Department of Information Technology, and the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, the state governments, and premier medical and technical institutions of India have taken initiatives with the aim to provide quality healthcare facilities to the rural and remote parts of the country. Startups, investors, and consumers were asking for regulations and guidelines regarding the procedure, reimbursement, quality of service, and privacy issues.
The Indian government’s guidelines for telemedicine solutions launched on March 25, 2020, were welcome. Previously, telemedicine operations were governed by several statutory guidelines. As per Section 27 of the Medical Council of India Act, 1956, any person who is enrolled in Indian Medical Register, could practice in any state of India. Hence, inter-state telemedicine service is legal, though it has not been formalized.
The current telemedicine guidelines in India provide a more comprehensive framework for applications, mode of communication, medical ethics, data privacy and confidentiality, document requirements, fees, process, drug list, technological platforms, and more. The regulatory framework will also attract more investors to the telemedicine segment as businesses will have clarity for business models.
With the pandemic not relenting, it seems as if the medical community had only held back because of the lack of legislation to enable tele consultations. For no sooner was the policy announced than hospitals and clinicians hurried to jump onto the bandwagon, advertising contact information for patients.
According to DataLabs, the telemedicine market in India is expected to reach USD 5.4 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 31 percent. Startups such as Practo, DocPrime, mFine, CallHealth, and Lybrate were operating telemedicine services in India under a regulatory grey area. More hospitals and doctors are expected to line up to teleconsult on the platforms. Portea Medical, which provides home healthcare support through nurses and doctors, also plans to scale its teleconsulting business.
The COVID-19 pandemic and the ensuing lockdown have already led to rising demand for their services. mfine has seen patient volume growing fourfold, and hundreds of queries from hospitals. Practo has received requests from a large number of hospitals and clinics to make the online consultation services live for them, so that they could continue providing consultations to their patients online.
Recently, AarogyaSetu app maker, NITI Aayog and the office of the Principal Scientific Advisor to the PM, have launched a new initiative Swasth, on a standalone website, AarogyaSetu Mitr. The site aggregates telemed services.
AarogyaSetu Mitr offers doctor consultations, ePharmacy, and home lab test services. The company has partnered with eSanjeevaniOPD, Swasth, StepOne, Tata Bridgital Health, and Tech Mahindra’s Connectsense TeleHeath platforms to offer online consultation from a large group of doctors. Home lab tests are offered by third-party partnerships like 1mg, Dr. Lal PathLabs, Metropolis, SRL Diagnostics, and Thyrocare. The fact that Swasth links to the Aarogya Setu app is promising.
Global scenario
The global telemedicine market size is estimated at USD 41.4 billion in 2019, and is expected to witness a CAGR of 15.1 percent over the next five years, says a Grand View Research study. The WHO has mentioned telemedicine as one of the essential services in the policy to respond to the COVID-19 emergency.
Healthtech funding in India |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2014–2019 |
|||||
| Startup | Year | Founders | Total funding (USD mn) | Funding stage | Investors |
| Practo, Bengaluru | 2008 | Shashank Nd,Abhinav Lal | 195 | Late Stage (Series E) | Tencent, Ru-Net, Rsi, Fund, Thrive Captial, Trifecta Capital |
| DocPrime, Delhi | 2018 | Ashish Gupta | 50 | Seed Stage | Policybazaar Group |
| Mfine, Bengaluru | 2017 | Ashutosh Lawania, Prasad Kompalli | 27.8 | Growth Stage (Series B) | SBI Holdings. SBI Ven Capital, Beenext. Stellaris Venture Partners. Prime Venture Partners. Alteria Capital |
| CallHealth, Hyderabad | 2013 | Shailendra Kumar Komatreddy, Sandhya Raju, Hari Thalapalli | 14 | Growth Stahe (Series B) | The Times Group, Sachin Tendulkar, PV SIndhu, Pullela Gopichand |
| Lybrate, Delhi | 2013 | Saurabh Arora | 11.43 | Growth Stage (Series A) | Nexus-Venture-Partners, Tiger Global Management, Ratan Tata, Nexus Venture Partners |
| ADI Media Research | |||||
Technology insights. The industry is driven by three concepts that include real-time (synchronous), store-and-forward (asynchronous), and others like home health virtual medicine. Real-time telemedicine refers to the contact between patient and healthcare practitioner via the use of electronic mediums, majorly video conferencing. This concept, also referred to as synchronous telemedicine, entails vast amount of application, which varies from a simple telephonic conversation to a complex robotic surgery.
On the other hand, store-and-forward system does not occur in real-time and involves the storage and transmission of medical information to the practitioner at a convenient time. Home health-based telemedicine involves patient monitoring from a distant location in an effort to control unnecessary hospital expenses. Increasing demand for improved quality and safety by the application and demand for mobile technologies, clubbed with adoption rate of home care, is anticipated to fuel the demand for telemedicine.
 Component insights. The software telemedicine segment is expected to witness significant growth. The hardware segment dominated the market in 2019, and includes medical peripheral devices, webcams, speakers, microphones, display screen, videoconferencing devices, laptops, and monitors.
Component insights. The software telemedicine segment is expected to witness significant growth. The hardware segment dominated the market in 2019, and includes medical peripheral devices, webcams, speakers, microphones, display screen, videoconferencing devices, laptops, and monitors.
Services are further classified into monitoring, consulting, and academic applications of telemedicine. The tele-monitoring segment held the largest revenue share in 2019, and is expected to witness a steady growth in the near future.
Application insights. The teleradiology segment accounted for the largest share of the global telemedicine market in 2019. The dominant share of this segment can be attributed to factors like increase in imaging practices, workflow adoption by healthcare providers, and the streamlining and regulation of teleradiology practices.
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into teleradiology, implementation of picture archiving and communication system (PACS), and growing R&D activities pertaining to eHealth are the key factors driving the market growth.
Delivery model insights. Web/mobile-based delivery model is expected to witness significant growth in coming years as it offers direct access to care delivery solutions. This segment is further categorized into telephonic and visualized access to the care. Telephonic care delivery dominated the market owing to its benefits such as cost-effectiveness and ease of operation. In addition, rising smartphone penetration and disposable income are augmenting the segment growth.
On the other hand, increasing awareness among users regarding telemedicine, introduction of technologically advanced solutions, and penetration of cloud-based solutions are anticipated to boost the adoption of visualized care delivery solution in coming years. Rising need for immediate medical assistance to patients located in remote locations is fueling the adoption of video conferencing telemedicine solutions. Key market players are also focusing on continual product innovation, such as cloud-based and mobile video conferencing.
End-use insights. The providers segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2019, owing to increased adoption of remote monitoring devices in old age and chronically ill patients, advancements in tele-monitoring devices, and the variety of tele-specialty services offered.
Telehealth solutions improve healthcare quality and offer convenience for healthcare providers in terms of quick access to patient records, improved decision support, providing clinical alerts, and real-time quality reporting. eHealth solution offers great convenience to healthcare professionals in terms of patient workflow and data management, which are expected to boost the usage of telemedicine by providers over the forecast period.
Type insights. The tele-hospitals segment held the largest share in 2019, and is expected to expand at a steady growth rate. Telemedicine services are generally preferred in emergency care. As the role of eHealth services expands in healthcare, hospitals can use telemedicine for urgent care, primary diagnosis, and second opinions. It can help rural hospitals to provide 24/7 virtual assistance, small hospitals to share the night coverage cost, and offer better post-discharge facilities. These expanding tele-hospital applications are contributing to the growth of this segment.
Tele-homecare solutions are projected to register significant growth in coming years as adoption of remote patient monitoring devices is increasing. Favorable government initiatives, increasing awareness among patients toward their health, and high penetration of internet-based solutions are some of the factors attributing to the segment growth.
Regional insights. North America dominated the global market owing to high demand for telemedicine in the recent past, followed by Europe. Developing regions such as Asia-Pacific and Middle-East and Africa are expected to experience positive growth owing to rapid demand for telemedicine and healthcare assistance, especially in the rural areas.
Market share insights. Prominent industry participants include Teladoc; Doctor on Demand; iCliniq; IBM; Intel Corporation; Philips Healthcare; McKesson Corporation; AMD Telemedicine; GE Healthcare; CardioNet Inc.; 3m Health Information Systems; Medic4all; CirrusMD Inc.; Cisco; and American Telecare Inc.
Vendors are investing in research and development to generate technologically advanced systems in order to gain a competitive advantage over other suppliers and provide economic benefits to the industry. The market is expected to become highly competitive as many startups are seeking opportunities in this sector.
Moreover, with the COVID-19 pandemic, technologists and manufacturers have a huge opportunity to upend the healthcare industry with enhanced quality and affordable services that are easily accessible to everyone. This is further anticipated to put telemedicine services on a positive growth trajectory in the coming few years.
Outlook
It might just be the case that telemedicine is experiencing a bubble, which will burst post-COVID-19. Under normal circumstances, regulations and pricing issues might stifle its growth as it has been the case so far. The technology might recede back into oblivion, only to rise up again during the next outbreak.












