Molecular Diagnostics
MDx, the best is yet to come

Ongoing advances will continue to shape MDx landscape, not only from a technical perspective but also with interconnected logistical, financial, and regulatory factors that are critical to modern healthcare delivery. In short, MDx revolution shows no signs of slowing.
Molecular diagnostics (MDx) market outlook has witnessed several advancements over the years, owing to robust efforts from industry players to develop innovative products, and achieve commendable market share. Research studies pertaining to molecular diagnostics solutions have offered a deep insight of molecular attributes to the healthcare industry to facilitate a better understanding of human health, and develop care standards for diagnosis of diseases.
The introduction of NAAT (nucleic acid amplification test) devices has given healthcare professionals access to more advanced diagnostic tools. Since these tools possess high specificity, sensitivity, and offer superior-quality results, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has certified NAAT as the gold standard for the diagnosis and detection of various ailments, such as influenza, malaria, and trichomonas. This in turn is likely to present lucrative growth prospects for the global market outlook in the forthcoming years.
Molecular testing on Covid-19 is paired with declines in more traditional molecular tests as patients avoided doctors and continued to reduce in-person doctor visits during lockdown. Down-but-not-out segments include cancer, histology, and inherited diseases, which are expected to continue to grow, perhaps surge, in coming years. Prior to Covid-19, liquid biopsy was one of the stars of this segment. New LDT tests in inherited disease testing, using IVD supplies, which includes non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), is driven by the demand in China. Even though the demand is for laboratory test services, and not for IVD products, the demand for instruments, kits, and consumables that are approved by regulatory agencies is driving the segment. However, the market opportunities may be challenging to access by foreign IVD companies due to the regulations promoting domestic companies.
The molecular diagnostics field worldwide, up until recently, has been dominated by large firms like Roche, followed by Cepheid/Danaher, bioMérieux, Qiagen, Hologic, BD, Siemens, and Luminex. While many of these companies are focused on competitive strategies as sophisticated automation for molecular testing, and test menu expansion to maintain their position, emerging competitors are also entering the market by developing next-generation technologies.
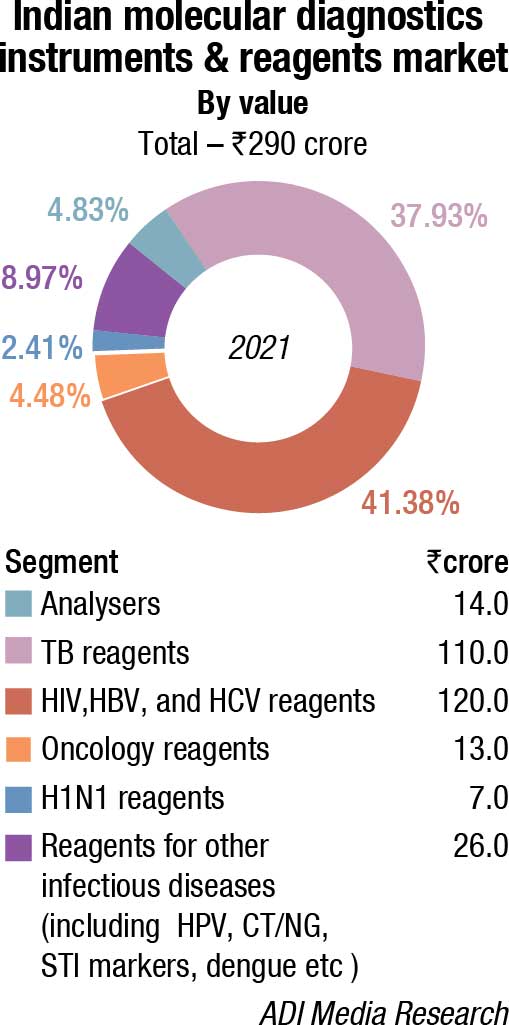
The Indian molecular diagnostic market in 2021, sans Covid testing, is estimated at ₹290 crore, a 9.8-percent increase over 2020. This growth trend is expected to continue over the next couple of years. Some traction was observed in demand for TB reagents; HIV, HBV, and HCV reagents, and a miniscule increase in reagents for oncology testing. The demand for analyzers remained steady.
While reliable estimates are not available for the value of analyzers procured in 2021 for Covid testing, one estimate suggests that the market in 2021 was in the vicinity of ₹8000 crore. This includes extraction machines, extraction kits, amplification test equipment, rapid molecular test kits, and RT-PCR kits.
| Indian molecular diagnostics market | |
| Leading players – 2021 | |
| Segment | Some leading companies |
| Analyzers | Roche, Abbott, Thermo Fisher, Qiagen, Danaher, and Randox |
| TB reagents | Danaher, Molbio, Qiagen, and Bio-Rad |
| HIV, HBV, and HCV reagents | Abbott, Qiagen, Roche, and Altona |
| Oncology reagents | Qiagen, 3B BlackBio Biotech, Roche, and Siemens (Fast Track) |
| H1N1 reagents | Siemens (Fast Track), Qiagen, and Hi-Media |
| Reagents for other Infectious diseases (including HPV, CT/NG, STI markers, dengue etc) | Bio-Rad, PerkinElmer, Beckman Coulter, bioMérieux, Tulip Diagnostics, CPC, and Medsource Ozone |
| ADI Media Research | |
In the first two years of Covid, regular molecular tests were on the back burner, and momentum picked up only from July 2021. The PLHIV (viral load testing for all people living with HIV/AIDS) Program, announced in February 2018 providing free-of-cost testing for 1.2 million HIV patients, had suffered a setback in the pandemic.
The Covid-19 pandemic severely disrupted tuberculosis control efforts, and services too. Resources dedicated to identifying and treating tuberculosis were diverted to the Covid response, with direct effect on tuberculosis programs. Similarly, measures to prevent Covid-19 transmission, such as lockdowns, made it harder for people to access tuberculosis testing and care. As a result, there was a drastic decline in the number of people who were newly diagnosed and treated for tuberculosis and an increase in deaths from tuberculosis for the first time in more than a decade. These tests saw a restoration to somewhat normalcy in the latter half of 2021.
While 2022 has seen a revival of the regular molecular tests, the 918 labs conducting TrueNat tests and 126 labs for CBNAAT tests set up for Covid-19, are now lying almost idle. Late 2020 and 2021 had seen stabilization of supply chains for Covid-19 testing, establishing a strong market, particularly for NAATs. Later, the development of rapid antigen detection tests and point-of-care NAATs saw the market shift away from the test base previously dominated by high-volume, core laboratory-based NAATs. The Covid-19 PCR tests conducted at 2302 labs are expected to contract beyond 2022. These had already in some cases made way for the faster rapid molecular tests, LAMP, when the presence of an active infection is detected by targeting specific gene sequences of SARS-CoV-2. Barring the rise of a more severe virus variant, PCR testing is expected to experience a plateau in the short term due to successful efforts in public vaccination campaigns. Currently, 44 labs are doing other molecular nucleic-acid tests. This is a total of 1450 government labs and 1940 private labs, as of September 2022.
As the need for Covid-19 testing is now collapsing to a fraction of its current demand, molecular diagnostics companies will be holding and maintaining facilities that can create immense supply. This mismatch between demand and supply will either lead to a collapse in prices of molecular diagnostic tests, as suppliers struggle to break even on their facilities maintenance costs, or a mass selloff or repurposing of these facilities.
The global Covid-19 pandemic had accelerated these and other new approaches for molecular diagnostics to enter the market through substantially reduced regulatory hurdles, with many novel technologies coming out of research laboratories.
Either way, the companies in the molecular diagnostics space will have to plan their next steps very carefully. They have made a lot of money in the boom of the Covid-19 pandemic, but they must be careful not to be saddled with large illiquid material assets for a market that is a fraction of its previous price.
In 2022, the government buying continues to remain a question mark. Since the Covid outbreak, funds were diverted to pandemic related equipment. With the pandemic receding, the thrust on Make in India initiative has held back procurement of high end, niche equipment.
Deal making was strong among molecular diagnostics players during 2021 despite the continuation of the pandemic, with most merger and acquisition (M&A) transactions demonstrating either a pivot in a new direction or an enhancement of current portfolios. In comparison to acquisition activity in the space in 2020, overall deal value for 2021 was lower, but deal volume tripled. Financings also saw an uptick in deal numbers as well as an increase in deal value compared to the previous year. Investors’ confidence was showcased through both public and private fundraising, particularly for personalized medicine and liquid biopsy-focused companies.
![]()
In 2021, molecular diagnostics companies agreed to 24 mergers and acquisitions, which had an aggregate deal value of USD 9 billion versus USD 13.2 billion from only eight transactions in 2020. Deal activity in terms of both volume and value was the strongest during Q1, with nine deals together valued at USD 4.5 billion (half the full-year total). There was a decrease in Q2 with seven deals together totaling USD 3.4 billion, but Q3 (three deals) and Q4 (five deals) did not even reach one billion dollars, with USD 300 million and USD 728 million in aggregate values, respectively.
|
Top ten molecular diagnostic M&As – 2021 By value (USD mn) |
|||
| Acquirer | Target | Deal value | Deal summary |
| Roche | GenMark Diagnostics | 1832 | Roche purchases GenMark to enhance Roche’s presence in the infectious disease diagnostics space and bring the company into the syndromic testing market. |
| DiaSorin | Luminex | 1800 | DiaSorin acquires Luminex, a global provider of molecular diagnostics specializing in multiplexing technology. |
| Hologic | Mobidiag | 714 | Hologic buys Mobidiag, a firm that develops and markets PCR-based tests for acute conditions including gastrointestinal and respiratory infections, and antibiotic resistance. |
| Agilent | Resolution Bioscience | 695 | Agilent buys Resolution Bioscience and gains next-generation sequencing-based precision oncology diagnostics to support both the biopharma services market and the clinical cancer testing market. |
| Veracyte | Decipher BioSciences | 600 | Veracyte acquires Decipher to further solidify its global leadership in the genomic cancer diagnostics market, gaining a portfolio of urologic cancer diagnostics that use whole-transcriptome analysis and machine-learning-based algorithms. |
| LabCorp | Personal Genome Diagnostics | 575 | LabCorp agrees to acquire Personal Genome Diagnostics, a cancer genomics company with a portfolio of liquid biopsy and tissue-based products and services. |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific | Mesa Biotech | 550 | Thermo Fisher buys Mesa Biotech, a firm that develops and commercializes the Accula PCR-based rapid point-of-care testing platform available for detecting infectious diseases, including SARS-CoV-2, influenza A and B, respiratory syncytial virus, and group A Streptococcus. |
| NeoGenomics | Inivata | 390 | NeoGenomics acquires liquid biopsy company Inivata and gains access to a platform that unlocks essential genomic information from a simple blood draw to guide and personalize cancer treatment, monitor response, and detect relapse. |
| Bio-Techne | Asuragen | 320 | Bio-Techne buys Asuragen including its US FDA-cleared AmplideX Fragile X syndrome diagnostic and carrier screening kit as well as its QuantideX quantitative PCR (qPCR) BCR-ABL IS kit to enable the monitoring of leukemia patients for minimal residual disease. |
| Veracyte | HalioDx | 308 | Veracyte acquires immuno-oncology diagnostics firm HalioDx, gaining a portfolio of immune assessment solutions. |
| Nature | |||
The outlier in Q1 2021 in terms of deal value was Roche and its USD 1.83-billion all-cash purchase of GenMark Diagnostics in a transaction that will enhance Roche’s presence in the infectious disease diagnostics space (especially in respiratory and bloodstream infections) and bring the company into the syndromic testing market for the first time. GenMark’s ePlex system drives lab efficiency through streamlined order-to-reporting workflow, and enables better patient outcomes by rapidly diagnosing a patient’s symptoms. The company’s Respiratory Pathogen Panels identify the most common viral and bacterial organisms associated with upper respiratory infection, including SARS-CoV-2, complementing Roche’s extensive portfolio of Covid-19 diagnostics solutions.
In a similarly high-value deal in Q2, DiaSorin paid USD 1.8 billion in cash to buy Luminex and its extensive test offerings in the infectious disease, respiratory, vector-borne, hospital-acquired, and gastroenterology infection markets, as well as genetics products and women’s health diagnostics. Its business includes molecular tests for infectious diseases with single-analyte/low-plex real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology, as well as a solid multiplexing panel technology for pathogen identification. The life sciences segment includes the licensed technologies group, which provides the xMAP technology for performing a wide range of protein and nucleic-acid-based multiplex assays on a single platform to more than 80 partners, and a flow cytometry business developed from its January 2019 acquisition of EMD Millipore’s flow cytometry portfolio. In terms of technologies, life sciences accounted for most of Luminex’s USD 417 million in 2020 revenues, followed by MDx multiplexing.
For the year, just those two deals hit the billion-dollar mark, but 13 other transactions reached USD 100 million or more.
Roche was one of the three companies that closed more than one acquisition. In addition to the GenMark purchase, Roche also acquired the TIB Molbiol Group, a company that specializes in ultra-rapid assay development for emerging infectious diseases, including SARS-CoV-2 variants. The two other multi-deal players included Veracyte and Hologic. Veracyte held two spots on the list of top-10 deals by value with its purchases of Decipher Biosciences (urologic cancer diagnostics) for USD 600 million in cash, and HalioDx (immuno-oncology diagnostics) for USD 308 million. Hologic also held a top-10 spot with its USD 714-million buy of PCR test developer Mobidiag, and also buying of European molecular diagnostics and epigenetics firm Diagenode for USD 159 million, in addition to women’s health MDx company BioTheranostics for USD 230 million.
Financing activity. During 2021, molecular diagnostic financings – including debt, follow-on public offerings (FOPOs), initial public offerings (IPOs), private investments in public equity (PIPEs), and venture capital (VC) funding – reached an aggregate of USD 8.8 billion from 73 transactions versus USD 7.6 billion in 2020 from 55 deals. The year opened strongly with 30 financings, totaling USD 4.2 billion in the first quarter, but the deal volume was lower for the other three quarters and deal value decreased over the year, with USD 2 billion in Q2 (17 deals), USD 1.8 billion in Q3 (12 deals), and USD 768 billion (14 deals) in Q4.
|
Venture capital investments in liquid biopsy companies – 2021 |
||
| Company (products/platform) |
Financing round |
Amount raised (USD Mn) |
| Exai Bio (combines oncRNA technology with machine learning and AI to decipher tumor signals) |
Series A |
67 |
| Rarecells (ISET circulating tumor cells platform applies AI algorithms to immunomorphological cellular profiles and altered genome-wide DNA characteristics) |
Series A |
5 |
| Alamar Biosciences (leverages NGS using ultra-high sensitivity and massively parallel scale for proteomic analysis) |
Series B |
80 |
| InterVenn Biosciences (Dawn assay for immune checkpoint inhibitor response prediction; glycoproteomics biomarker interrogation platform uses AI and mass spectrometry) |
Series C |
201 |
| SAGA Diagnostics (ultrasensitive SAGAsign hybrid method using technologies based on digital PCR and NGS for MRD monitoring) |
Series A2 |
12 |
| Caris Life Sciences (molecular intelligence approach uses whole exome sequencing, whole transcriptome sequencing, protein analysis, and AI models and signatures to assess genes in both DNA and RNA) |
Undisclosed |
830 |
| Nucleix (Lung EpiCheck uses circulating tumor DNA methylation technology for early detection of lung cancer) |
Undisclosed late-stage |
77 |
| Personal Genome Diagnostics (elio products for tissue- and liquid biopsy-based genomic testing) |
Series C |
103 |
| Inivata (RaDaR, a highly sensitive personalized assay for detection and monitoring of MRD and recurrence) |
Series C |
35 |
| Delfi Diagnostics (machine-learning approach for genome-wide fragmentation profiles of cell-free DNA) |
Series A |
100 |
|
Informa’s Biomedtracker 2022 |
||
Late-stage VC rounds (series C and later) brought in most of 2021’s financing dollars, with 18 transactions representing 30 percent of the annual aggregate and together totaling USD 2.6 billion. Early-stage rounds captured just 6 percent of the 2021 dollars, with 13 transactions reaching a total of USD 552.5 million.
Overall, there were nine MDx players raising USD 100 million or more in late-stage rounds. The largest transaction in this category, and also the biggest MDx financing of the year, was achieved by Caris Life Sciences, which brought in USD 830 million through a late-stage growth equity round in Q2, making up 41 percent of the second quarter’s total financing alone. Caris is engaged in molecular profiling that assesses DNA, RNA, and proteins to reveal a molecular blueprint to inform more precise and personalized treatment decisions. The funding provides the company with the capital for continued commercial expansion and investment toward delivering a first-in-class liquid biopsy platform across all cancer types.
During 2021, there were ten players overall in the liquid biopsy space raising money across both early- and late-stage vehicles.
During 2021, 13 companies went public in the molecular diagnostics space, accounting for USD 1.9 billion (22% of total financing). Eight IPO transactions reached or exceeded the USD 100-million mark, led by New Horizon Health, which netted USD 282.5 million in its listing on the Hong Kong Exchange. ColoClear incorporates its multi-target FIT-DNA platform, which utilizes quantitative PCR and a fecal immunochemical test method to detect the presence of a KRAS gene mutation in stool and hemoglobin, enabling a high sensitivity for precancerous lesions. Pupu Tube is a FIT screening diagnostic to detect hemoglobin biomarkers associated with colorectal cancer in stool.
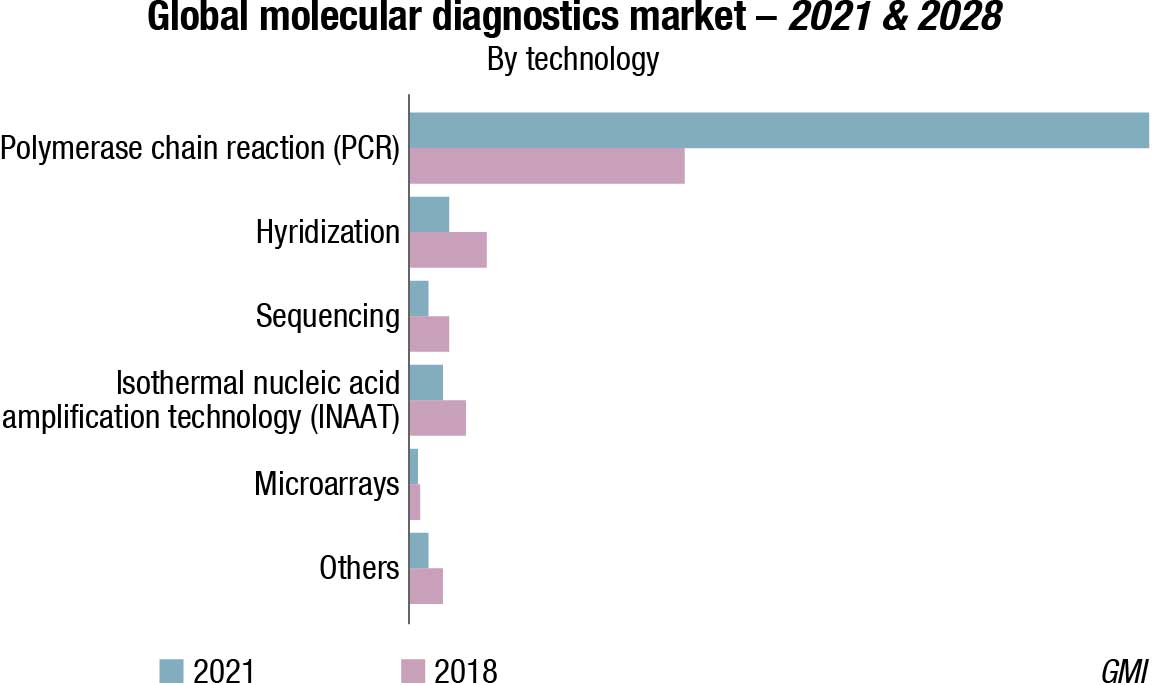
The global molecular diagnostics market size was valued at USD 37.04 billion in 2021 and is expected to decline at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of −1.6 percent from 2022 to 2030. The shrinking of the market can be attributed to the decline in demand for molecular Covid-19 testing over the next 8 years. However, factors, such as technological advancements, rising elderly population, and increasing demand for genetic testing is boosting the growth of the market. In addition, rising demand for PoC testing can be attributed to increasing demand for self-testing diagnostics, and patient awareness about faster diagnostics.
The reagents segment accounted for the largest revenue share of the market in 2021. It is expected to maintain its dominance in upcoming years owing to its wide adoption in research and clinical settings. Standard reagents help achieve efficient and accurate results. Standardized results, improved efficiency, and cost-effectiveness are anticipated to support the market growth.
Furthermore, the growing use of instruments to detect coronavirus, which were earlier developed for other infectious diseases, is anticipated to boost the market growth. For instance, in February 2022, Roche Diagnostics extended its Covid RT-PCR tests portfolio to the new cobas 5800 system in countries that accepted the CE mark approval.
Central laboratories held the largest share of the market in 2021, attributable to high procedure volumes for Covid-19 testing in central laboratories. An increase in the number of initiatives undertaken by the government to provide various services, such as reimbursement for diagnostic tests, is another major factor anticipated to drive the market.
There is an increasing interest in the development of molecular diagnostic platforms that can also be used in POC settings. Therefore, various companies are designing assays and molecular diagnostic platforms for POC or near-patient testing. In addition, the growing development of new assays that offer quick POC results is anticipated to boost market growth.
The PCR segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2021. This is attributed to its use in the detection of Covid-19 and other infectious diseases. The increasing use of high-throughput PCR technology to detect infectious diseases and genetic diseases is expected to drive market growth. Sequencing technologies for the molecular diagnostics market include DNA sequencing processes and emerging NGS technologies, such as sequencing platforms and RNA sequencing. DNA sequencing technologies are integrally linked to drug discovery, novel drug development, and personalized medicine. Companies are launching new NGS-based tests for early disease diagnosis.
Vendor updates
Prominent key players operating in the molecular diagnostics industry include Abbott Laboratories, Agilent Technologies Inc., Becton, Dickinson and Company, Biocartis, bioMérieux SA, Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc., Danaher Corporation, F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Hologic, Inc., Illumina, Inc., Qiagen, Quidel Corporation, Siemens Healthineers AG, Sysmex Corporation, and Thermo Fisher Scientific, among others. These market participants are implementing various growth strategies, collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions to enhance product capabilities to sustain market competition.
In May 2022, Qiagen N.V. announced the launch of the therascreen EGFR plus RGQ PCR kit, a new IVD test for sensitive epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation analysis, detecting all currently known activating and resistance EGFR mutations. The real-time qPCR test builds on the established therascreen EGFR RGQ PCR kit and provides improved limits of detection, quicker turnaround times, automated sample-extraction options, and automated results analysis.
In May, BD (Becton, Dickinson, and Company) too announced the US launch of its new, fully automated, high-throughput infectious disease molecular diagnostics platform. The BD COR MX/PX system integrates and automates the complete molecular laboratory workflow, from sample processing to diagnostic test result for large, high-throughput labs.
In January 2022, Biodesix announced the launch of its GeneStrat NGS™ Test, a blood-based tumor profiling test, to guide physicians in treating advanced lung cancer based on mutations.
In January, Seegene too announced the launch of its upcoming Allplex SARS-CoV-2 fast PCR assay. The test has a turnaround time of 60 minutes and thus is suitable for mass testing.
In November 2021, EKF Diagnostics acquired Advanced Diagnostic Laboratory LLC, or ADL Health, a high-complexity PCR-focused testing laboratory. ADL Health, based in San Antonio, provides Covid-19 testing for dozens of Fortune 500 companies and government agencies, such as Air Canada and United Airlines.
In February 2021, Thermo Fisher Scientific introduced a manufacturing facility in Bengaluru. This state-of-the-art manufacturing facility will produce Applied Biosystem’s CoviPath RT-PCR testing kits and MagMAX Dx prefilled viral/pathogen nucleic acid isolation kits.
In recent years, uptake of PCR MDx has experienced substantial increase. PCR tests are highly effective in detecting pathogenic DNA for several contagious diseases. Efforts are underway to improve the scope of PCR and RT-PCR tests to discover treatments for life-threatening ailments.
The Covid-19 pandemic has especially bolstered prospects for the expansion of the PCR and real-time PCR molecular diagnostics market size. Various healthcare settings have deployed real-time (qPCR) and digital (dPCR) PCR tests to detect and diagnose possible cases. Its highly sensitive nature has led healthcare providers to adopt PCR tests on a large scale. On the back of such trends, the global PCR and real-time PCR molecular diagnostics market is set to reach new heights, surpassing an impressive revenue threshold in the coming decade.
Real-time PCR tests are likely to retain lucrativeness, attributed to higher sensitivity, timely processing of test results, greater precision, and less prone to contamination, thereby limiting error margins. Uptake of RT-PCR tests has specifically surged amid the Covid-19 pandemic.
Likewise, digital PCR tests are acquiring traction, owing to increasing smart technology penetration across the healthcare sector. Digital PCR tests do not require calibration against standards, an aspect that is important for RT-PCR tests. Moreover, dPCR tests can also detect more samples as opposed to traditional PCR tests.
Testing for infectious diseases is likely to attain high growth, attributed to high prevalence of sexually transmitted infections, respiratory infections, and hepatitis C and B, respectively. Immense traction is expected related to this for the PCR and real-time PCR molecular diagnostics market in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Simultaneously, oncology is emerging as a key application area. Continuous innovations and technological breakthroughs are likely to enhance PCR molecular diagnostics in the detection, diagnosing, and treating cancers on a large scale. An impressive revenue share is projected for the segment in the global PCR and real-time PCR molecular diagnostics market.
Consumables and reagents are likely to remain primary PCR molecular diagnostic products until 2030. The launch of new PCR testing kits in recent years to identify and detect pathogen presence across various end-use industries is uplifting their growth.
Hospitals will remain the primary PCR molecular diagnostics technology end-users, owing to high preference by patients to seek professional treatment. Hospitals possess the necessary qualified personnel capable of conducting such complicated tests and provide precise results. Recently, diagnostic labs and academic and research institutions have also been demanding advanced molecular diagnostics to streamline their research and testing capacities. These settings provide an ideal environment for technicians and students to acquaint themselves with the latest diagnostics technology through trial and error.
CR and RT-PCR tests are finding significant ground amid increasing incidence of chronic and infectious diseases. According to WHO, cancer is the leading cause of frailty and deaths around the world.
RT-PCR tests have, therefore, proven extremely useful in identifying numerous small tumor cells circulating within the human body. These tests assist in providing accurate prognosis and predict resistance, toxicity, or response to chemotherapy. Likewise, the test is also used to detect HIV/ADIS and Hepatitis C, respectively.
With increased complications of chronic and infectious ailments, the demand for sophisticated diagnostic tools to address them has taken precedence. Timely detection is important to manage and stem further spread of diseases, such as cancer. Clinical benefits, such as enhanced sensitivity, broader application, and better turnaround times are accelerating the uptake of advanced molecular diagnostics. Based on this trend, the demand for PCR and RT-PCR tests is likely to proliferate in the coming years, bolstering the growth of the PCR and real-time PCR molecular diagnostics market.
Considering the detection of highly infectious pathogens, including 2019-nCoV, must be performed in biosafety laboratories ranked Class II or above, the inspectors must be fully prepared and cautious to maintain work efficiency. In the multi-country effort to combat the 2019-nCoV epidemic, multiple inspectors have been infected. Therefore, the development of a fully automated, fully-enclosed, integrated detection system from sample extraction to signal amplification and detection is crucial to avoid high-frequency contact between the inspector and infectious samples. This is a crucial step in improving the ability to detect highly infectious pathogens.
In the future, the application of genomic technology for the detection of clinically critical and complex infections, particularly during outbreaks, need to be improved. This will aid in the early detection of epidemic pathogens, and early warnings of emergencies and emerging infectious diseases. In countries or regions, where conditions permit, metagenomics detection technology capabilities should be enhanced. Metagenomics detection technology can quickly obtain entire genome sequences and full-length genome sequenced of samples. This provides a more comprehensive pathogen gene-scanning analysis for critical and complex infections. The basis for diagnosis and differential diagnosis is to determine pathogen loads, identify drug-resistant genes, and guide clinical medication. However, metagenomics technology still needs to be optimized by enriching pathogen target genes, shortening testing times, simplifying the testing process, and reducing the cost of testing. Thus, metagenomics technology is due to become one of the routine clinical testing technologies.
During the 2019-nCoV pandemic, numerous suspected cases and medical observers were required to perform repeated nucleic acid tests. However, detection throughput, biosafety requirements, and the number of professional inspectors are limited for RT-PCR. Numerous grass-roots hospitals cannot perform this molecular diagnosis, resulting in many patients being unable to receive timely diagnosis. Therefore, it is essential to research and develop POCT technology and equipment for nucleic acids or proteins. In particular, POCT technology that employs sample-in result-out should be utilized as early as possible. This would solve the difficulty of numerous primary medical institutions being unable to perform rapid molecular diagnosis.
In the future, novel epidemics or pandemics may be inevitable. It is crucial that pandemic-prevention agencies perform further research on pathogen differential diagnosis technology to improve testing times, to provide definitive diagnoses, and to differentially diagnose diseases with similar clinical manifestations. There are various types of pneumonia-related pathogens, including influenza virus, parainfluenza virus, adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus, mycoplasma, and chlamydia. Considering RT-PCR results are time-consuming and laborious, there is an urgent need for medium-throughput detection technology for the differential diagnosis of 2019-nCoV and non-2019-nCoV conditions. In the future, it is necessary to focus on the development of high-throughput and low-cost differential diagnostic technologies. Furthermore, the development of detection technologies and supporting reagents that can simultaneously rapidly detect dozens of pathogens will be beneficial.












