Endoscopy Equipment
Resuming endoscopy in the wake of COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic had a vast impact and necessitated a worldwide response. Endoscopy falls squarely into that reality. Non-emergent, endoscopic procedures were among the many elective procedures suspended and that meant the endoscopist’s procedures had to be put on the shelf until officials had a better grasp on the coronavirus disease and the outlook for society improved.
Endoscopes have created a revolution in the practice of gastroenterology. They improved diagnosis enormously, enabled quicker, less invasive, and more cost-effective surgical treatment, while endoscopic screening has prevented many cancer deaths. The new technology stimulated research leading to a better understanding of gastrointestinal pathology, identifying new diseases, and clarifying the etiology of others. Better-controlled clinical trials accelerated the use of newer and more effective drugs. National and international endoscopy societies supported nursing input, encouraged research, stimulated specialist journals, and devised guidelines that encouraged audit and quality assurance.
Advances in instrument design and the manufacture of new accessories enhanced endoscopic technique, diagnostic ability, patient comfort, and safety. The risk of cross-infection inherent in the use of complex labile equipment that cannot be autoclaved remains a challenge. Endoscopy societies working closely with industry have established rigid protocols for high-level disinfection that minimize the risks, but strict adherence to guidelines and continued vigilance is essential, especially with the increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant commensals that can give rise to opportunistic infection.
Recently, each duodenoscope manufacturer, Fujifilm, Olympus, and Pentax currently marketing in the US was ordered by the FDA to conduct post-market surveillance studies to determine rates of contamination after clinical use and reprocessing of its fixed endcap duodenoscopes. Device design is a key factor that contributes to reprocessing challenges. The FDA believes the best solution to reducing the risk of disease transmission by duodenoscopes is through innovative device designs that make reprocessing easier, more effective, or unnecessary. For example, duodenoscopes that incorporate disposable components can facilitate cleaning, reduce contamination and reduce disease transmission following reprocessing. Disposable designs may reduce between-patient duodenoscope contamination by half as compared to reusable, or fixed endcaps. Government health departments have a responsibility to encourage and support research in this area by endoscopists, instrument manufacturers, and the pharmaceutical industry.
The COVID-19 pandemic is having a disruptive effect on the workflow and safety of gastrointestinal endoscopy units worldwide. Hospital closures connected to COVID-19 have cut into the sales of many medical device companies, but executives at rival makers of single-use scopes maintain the pandemic has only heightened existing concerns about contamination, exposure, and cost. Single-use scopes’ manufacturers contend that over the next decade, disposable scopes will account for a majority of devices sold, as they will perform better than traditional devices, cost less, and eliminate the risk of infection.
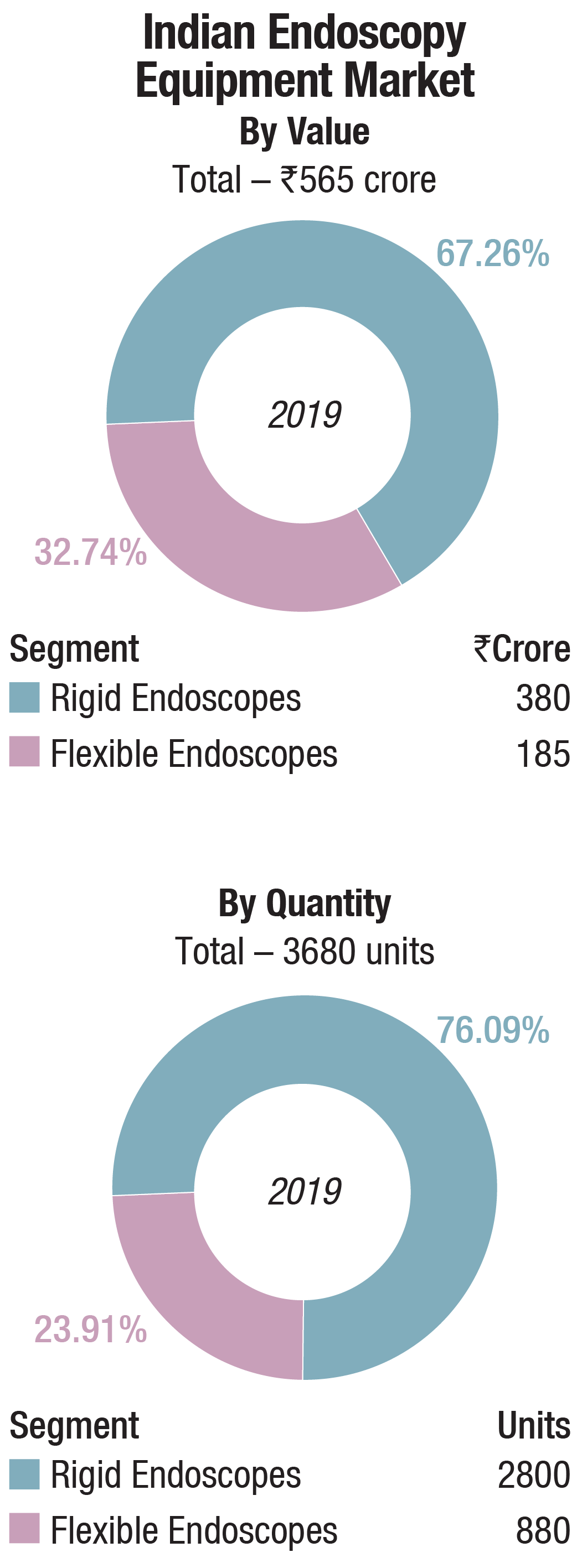
The Indian market
The indian endoscopes market in 2019 was dominated by the rigid models, with a 76 percent share by volume and a 67 percent share by value. The three leading players in the rigid endoscopes segment, Karl Storz, Olympus, and Stryker constitute 90 percent of the market combined. The local players continue to have a 10 percent market share. While the imported segment commands a unit price in the range of Rs 12-15 lakhs, the local players have to make do with Rs 7.5 lakhs. 
The flexible endoscopes segment is dominated by Olympus with an estimated 24 percent share by volume and a 32 percent share by volume in 2019. The other players in the reckoning are Fujinon and Pentax, neck-to-neck, scrambling for a 10 percent share each. The refurbished market has its niche customers, while Karl Storz has some loyal customers in Gujarat and North-East, with a handful of Chinese players also striving to keep their presence intact. Pentax has last some of its senior executives recently, and are in the process of appointing a distributor.
 As anticipated, 2020 has not been a great year for this segment. Endoscopy units in India are currently performing fewer than 10 percent of their usual procedures due to current restrictions With elective Surgeries being postponed, the demand for endoscopes has come down drastically, putting significant pressure on vendor margins. Elective cases are those where delaying an endoscopic procedure for 4–6 weeks is unlikely to affect the final outcome. Evaluations of chronic anaemia, dyspepsia and achalasia are some examples. Most of the screening and surveillance endoscopic procedures are also being deferred. Of course, there are exceptions as acute gastrointestinal bleeding and severe cholangitis with organ dysfunction that need an endoscopic procedure within 24 hours and infected pancreatic fluid collection and obstructing left colon tumour need an endoscopic procedure within 30 days.
As anticipated, 2020 has not been a great year for this segment. Endoscopy units in India are currently performing fewer than 10 percent of their usual procedures due to current restrictions With elective Surgeries being postponed, the demand for endoscopes has come down drastically, putting significant pressure on vendor margins. Elective cases are those where delaying an endoscopic procedure for 4–6 weeks is unlikely to affect the final outcome. Evaluations of chronic anaemia, dyspepsia and achalasia are some examples. Most of the screening and surveillance endoscopic procedures are also being deferred. Of course, there are exceptions as acute gastrointestinal bleeding and severe cholangitis with organ dysfunction that need an endoscopic procedure within 24 hours and infected pancreatic fluid collection and obstructing left colon tumour need an endoscopic procedure within 30 days.
The major reasons for the decrease in endoscopy procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic are fewer patients coming to the hospital due to government-mandated national lock-down, endoscopists themselves limiting the number of procedures due to the latest guideline recommendations for avoiding routine endoscopies, limiting contact with patients due to the fear of getting exposed, difficulty in managing usual patient volumes due to reduced availability of staff due to lockdown.
For instance, Medanta Hospital, Gurugram from an average of 80 endoscopy procedures is down to 25 procedures per day; Asian Institute of Gastroenterology, Hyderabad from 200 to 50 procedures; and AIIMS, New Delhi from an average of 100 per day to a mere 10 procedures. The government hospitals have reduced their buying, and corporate hospital chains have been at an all time low. Some demand is emanating for the mid-priced endoscopes, often from the dental schools and smaller new setups being established. Replacement buying is down to almost nil. Quite a few orders in the pipeline have been cancelled or have been kept on hold.
Global market
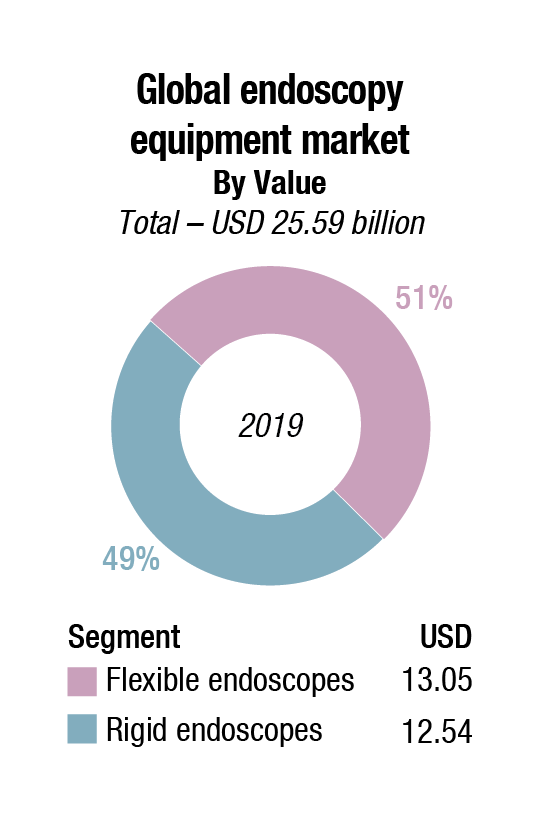
The global endoscopy equipment market is expected to reach USD 35.23 billion by 2024 from an estimated USD 25.59 billion in 2019 at a CAGR of 6.6 percent, estimates Markets and Markets. The key factors driving the growth of this market include growing demand for endoscopy procedures, growing investment, funds and grants, rising number of hospitals and growing hospital investments in endoscopy facilities, and technological advancements. However, unfavorable healthcare reforms and high cost of endoscopy procedures and equipment, and limited reimbursement in developing countries are expected to restrain the growth of this market.
 Minimally invasive surgeries are driving the use of various endoscopic procedures for diagnosis such as proctoscopy, gastroscopy, and cystoscopy. These surgeries require smaller incisions and hence offer advantages such as lesser pain, low or no risk of complications, and quicker recovery when compared to open surgery. They are also cost-effective and result in improved quality of life. The shift in trend from open surgery to minimally invasive procedures is expected to drive demand.
Minimally invasive surgeries are driving the use of various endoscopic procedures for diagnosis such as proctoscopy, gastroscopy, and cystoscopy. These surgeries require smaller incisions and hence offer advantages such as lesser pain, low or no risk of complications, and quicker recovery when compared to open surgery. They are also cost-effective and result in improved quality of life. The shift in trend from open surgery to minimally invasive procedures is expected to drive demand.
Increasing prevalence of cancer, that then require biopsies and endoscopic ultrasound is one of the key factors contributing to the growth of the market. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for an estimated 9.6 million deaths in 2018, which is estimated to increase to 22.0 million by 2034.
Emergence of endoscopic bariatric surgeries, namely, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty is also expected to drive the market. This procedure uses sutures for restructuring the stomach and helps reduce the stomach size by 70 percent. Although weight loss due to endoscopic bariatric surgery is not as effective as a surgical bariatric procedure, the former results in better health outcomes.
Owing to the effects of aging and the adoption of unhealthy lifestyles, disease burden is highest in geriatric patients. Furthermore, the geriatric population accounts for the maximum cases of cancer and chronic cardiovascular, respiratory, spinal, and neurological diseases. The economic impact of the geriatric population is much higher in developed nations as compared to emerging nations. This boosts the demand for various endoscopic procedures such as stomach, esophagus, cervical, orthopedic, and pulmonary endoscopy.
In 2019, flexible endoscopes dominated with a 51 percent share of the global endoscopes market. Their ergonomics features, increased safety and efficiency, and advancements in medical-optics technology drive the demand and consumption of flexible endoscopes. Increasing adoption of micro endoscopes, coupled with the rising trend of manufacturing smaller endoscopic devices, and consumer shift in preference to high definition (HD) and 3D systems are likely to boost the demand for flexible endoscopes globally. Moreover, several training centers have been set up to train medical professionals on using advanced flexible endoscopes, which drives the segment growth.
Among different types of flexible endoscopes, upper gastrointestinal endoscopes accounted for a significant share in 2019. Widening pool for patients suffering from gastric cancer and increasing demand for cancer screening are contributing to the growth of this segment. Various initiatives are undertaken by governments to create awareness regarding cancer detection and its diagnosis also drives the demand for different endoscopes.
On the other hand, the disposable endoscopes segment is expected to grow at a higher rate over the next few years on account of the increasing demand for single-use scopes for eliminating the risk of device-related infections. Device-related infections are a major health concern globally.
Advancements in optical imaging systems are expected to drive the adoption of flexible endoscopes in neuroendoscopy. Key players are conducting a number of programs to raise awareness about emerging neuroendoscopy techniques, which, in turn, influences the adoption rate of endoscopic devices for neurosurgeries. The growing prevalence of various cardiovascular diseases and the subsequent rise in diagnosis and treatment procedures lead to a higher usage rate of endoscopes in various cardiovascular surgeries.
North America dominated the market with a share of over 40 percent in 2019. This is attributed to developed healthcare infrastructure, high adoption of advanced technologies, and an increase in awareness about the advantages of minimally invasive therapies. High incidences of obesity and growing demand for minimally invasive bariatric surgeries are also some of the key drivers expected to positively affect the market. Moreover, the presence of organizations such as American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, which is dedicated to patient care and digestive health for promoting innovations in endoscopy, is expected to boost market growth.
A rise in the geriatric population and an increase in burden of chronic diseases such as cancer and GI diseases are driving the market growth in Europe. Moreover, technological advancements such as the development of micro-endoscopic and robot-assisted surgeries are driving the regional market growth. Various initiatives are undertaken by United European Gastroenterology (UEG) and European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) for creating supportive endoscopy services communities across Europe and promoting collaboration for providing safe, patient-centered, and accessible endoscopic care is expected to positively impact the market growth.
Asia Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest-growing market. Improving healthcare infrastructure, coupled with economic development in this region, has attracted foreign investment. Thus, key market players are developing strategies for expanding their business in this region. Moreover, rise in awareness about the advantages of minimally invasive surgeries over open surgeries and high chronic disease burden are expected to provide growth opportunities in this region. Aging population, particularly in China, is expected to further drive the market growth.
In recent years, the market has witnessed several product recalls, mainly due to reasons related to defects in equipment manufacturing processes. Frequent product recalls pose a major challenge for the growth of the endoscopy equipment market, particularly in the case of large players.
Some of the prominent players in the endoscopes market include Olympus, Karl Storz, Stryker, Boston Scientific, Ethicon, Fujifilm Corporation, Medtronic, Hoya Corporation, Richard Wolf GmbH, Smith & Nephew, Cook Medical, and B. Braun.
Technology trends
For years, the trend on improving the quality of endoscopy has been the launch of new models where the aim was: thinner and better looking. These developments have given scopes with an increasingly smaller diameter, thereby giving easier access and better patient satisfaction.
The image quality has been improved by the introduction of high definition (HD) imaging and advanced filter functions, where the light wavelength and their penetrations depths were utilized. These improved images have radically changed the endoscopist’s opportunities to perform real-time macroscopic histological diagnoses, and thereby making safer and more efficient clinical decisions.
Recently Artificial Intelligence, already popular in many other contexts, is finding its way in this segment too. In endoscopy the focus is on detection of neoplasia, and classification. The systems for AI were introduced in 2019, preliminary testing has already been done, and scientists are planning for more extensive tests.
The future of endoscopy is difficult to predict. However, industry is likely to see improvements in this field that currently seem almost unimaginable. The creative application of novel technologies from other disciplines has always enabled endoscopy (and indeed all aspects of minimally invasive surgery) to move forward. Imaging devices will certainly continue to decrease in size, such that microendoscopy will be feasible in the near future. Endoscopy of any luminal structure, including the vas deferens, will certainly follow.
Nanotechnology, including small robots built from novel materials, has already been demonstrated to be feasible. Self-assembling robots constructed from nucleotides have already been created. As has already been envisaged in science fiction, a time when small robots will patrol biologic structures to constantly survey and help protect normal anatomy and physiology is not difficult to imagine.
The incorporation of advanced physics and molecular biology techniques will almost certainly complement endoscopy, and are likely to eventually eliminate the need for endoscopy altogether. The first efforts to assimilate molecular biologic techniques into endoscopy have been made. Raman endoscopy consists of a powerful light-scattering technique used to identify the internal structure of molecules and crystals. Light of a known frequency and polarization interacts with and is scattered by a sample. The scattered light is then analyzed for its frequency and polarization, which can provide information on the characteristics of the sample.
Raman spectroscopy might greatly improve real-time histologic tissue diagnosis by measuring the molecular components of tissue in a qualitative and quantitative way. Light scattered by each tissue type has a characteristic spectrum, which can be used to generate a pseudocolor map; thus, by analyzing the tissue’s spectrum one will be able to tell if its composition is of a normal or a pathologic nature. The time needed to obtain such spectra is around 10–20s, which allows fast decision making that might enable real-time decisions as to whether to perform conservative or radical surgery, to define limits of resection or to differentiate benign from neoplastic tissue.
Another application of physics within endoscopy is optical coherence tomography (OCT). This imaging modality is capable of producing high-resolution, cross-sectional, subsurface tomographic imaging of the microstructure in biologic systems by measuring backscattered or backreflected infrared light. Its underlying physical principle is similar to that of B-mode ultrasonography, but instead of sound OCT applies light.
Industry Speak
Technological advancements and emerging trends in endoscopy
Velangini Reddy
Senior Deputy Product Manager–Gastroenterology,
Olympus Medical Systems
Endoscopy devices are constantly undergoing improvements due to the innovation and technological advancement continuously. Apart from the technology, other major growth driver that has led to the development of endoscopy devices market is a natural preference for less and non-invasive methods of treatment. Technological advancements offer low morbidity and mortality associated in the advanced therapeutic procedures unlike the conventional gastro surgical procedures.
Gastrointestinal malignancies continue to be the second leading cause of cancer–related deaths in the developed world. The early detection and treatment of gastrointestinal pre-neoplasms has been demonstrated to significantly improve patient survival.
Unfortunately, the poor sensitivity associated with white light endoscopy (WLE) is a significant limitation. In this regard, development of alternative diagnostic techniques like real-time optical chromoendoscopy offer significant improvements in the diagnosis of early lesions by allowing real time optical diagnosis targeted mucosal excisional biopsies.
The optical magnification capacity of specialized endoscopes is increased up to 520x and may provide optical biopsies of equivalent histological accuracy. This ability to detect subtle pre-neoplastic changes in the gastrointestinal mucosa in real time and improved staging of lesions could lead to curative endoscopic treatment of these lesions and, in the long-term, improve patient survival rates and quality of life.
Endoscopy market steadily increases its reach into therapeutic field, such as POEM/ESD and endoscopic bariatric procedures that previously were only performed through more invasive methods and now are treated through-the-scope.
Duodenoscopes with single use, disposable distal attachments are introduced recently, which elevate the standard of cleaning and care. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) has made many hepatobiliary procedures possible with echoendoscopes.
Disruptive technologies like motorized spiral enteroscope made the enteroscopy procedures easy, less time consuming, and complete with more therapeutic options. This led to more gastroenterologists opting to perform enteroscopy, which was earlier a time consuming and often incomplete procedure with the conventional balloon enteroscope.
In bronchoscopy, new technologies and innovations revolutionize the way pulmonologist were doing bronchoscopy. Modalities like radial EBUS, Cryo, BT, pleuroscopy open new avenues in respiratory field as well.
The promising future technologies for endoscopes are 4K imaging, bleeding detection technology, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for detection and diagnosis. These are expected to be available in near future.
OCT devices use a low-power infrared light with a wavelength of 750–1300 nm and images are generated from measuring the echo time delay and the intensity of back-scattered light. The depth of penetration of OCT imaging is approximately 1–3 mm, depending upon tissue structure, depth of focus, and pressure applied to the tissue surface. All the tissue layers of the bladder (urothelium, lamina propria, and muscularis propria) can be individually visualized by use of this technology according to their different light-reflecting properties.
Patients with other pathologies might benefit from the use of OCT to improve treatment and surgical decision making. For example, in the future, OCT may help to evaluate neurovascular bundle involvement in patients with prostate cancer and thus inform resection decisions. Similarly, OCT might be applied to kidney, ureter, and collection system tumors to help optimize resection.
Second Opinion
Making spinal surgery a success through minimal way
 Dr Nikhil Arbatti
Dr Nikhil Arbatti
Consultant Minimally Invasive & Endoscopic Spine Surgeon,
Nanavati Superspeciality Hospitals, Mumbai
Spinal surgery has come a long way, from its initial days, where the surgery was done for treating acute spinal problems leading to neurological symptoms, it has now entered an era, where spinal surgery is offered and performed for lifestyle related problems like back pain, leg pain, inability to walk or work. Thus the goal of spinal surgery is not only to relieve the patient of his acute or chronic problems, but to also improve his lifestyle.
Thus if spinal surgery is considered by patients nowadays, it is preferred if a keyhole/minimal invasive way of performing this surgery is available, so as to reduce the patient per-operative morbidity, and enhance the post-operative recovery.
The focus of spinal surgeons in association with medical device related companies is to devise ways in which a minimal invasive technique, with precision and accurate reproducibility is available.
Endoscopic and minimally invasive spinal surgery (MISS) is this step forward. MISS has grown exponentially in the last decade. This is mainly due to the development of extreme sophisticated optics, where the visualization which initially used to be with the naked eyes, is now done with advanced optics where the magnification is almost 39 times of the naked eye. This superior optics ensure that within a closed and reduced space also the visualization is more accurate and better.
Thus in MISS we use 16 mm or 19 mm tubes to perform all spinal procedures, and a 1.5 cm incision in the skin is all that is required to pass our instruments and reach up to the area where we need to operate, then with the help of microscopes we perform the entire surgery, with almost negligible complications.
In an endoscopic spine surgery, similarly we perform spinal surgeries with the help of scopes, these scopes are 6-8 mm in diameter, and are introduced with a 1cm skin incision. Also in an endoscopic spine surgery, we do not need to give any general anesthesia; it’s majorly done under local anesthesia.
As the patient is not given any heavy general anesthesia, post-operatively he undergoes early mobilization. This helps a lot to the patient in getting back to his routine activities quickly. Since majority of Spinal surgeries are performed for lifestyle related problems, the quick turnaround after an endoscopic spine surgery is truly welcome.
The benefit of endoscopic spine surgery is immense to the patient, with reduced hospital stay, reduced post-operative medications, and reduced intra-operative medications.
The requirement for an endoscopic spine surgery is also much cost benefit to the hospital, after one time investment in endoscopy Instruments, regular maintenance is what is required. The instruments if properly managed and cleaned will be able to be used for at least a considerable time. Thus the overall cost of an endoscopic spine surgery is much less than a routine open spine surgery.
Also once the Insurance companies start accepting this type of spine surgery as routine, and then cashless authorizations for such surgeries will also be applicable.
With the spine surgery market increasing year on year in india, not only because of availability of competent and world class infrastructure and facilities, but also because of affordability. India is poised to become a global hub of medical tourism.
The focus in such a scenario is not only to offer infrastructure and facilities which are world class, but also to offer cutting edge surgeries and outcomes which are comparable to any institute worldwide.
Endoscopic spine surgery is thus poised to take that step forward in spinal surgery.
Outlook
Endoscopy is a high-level aerosol-producing procedure akin to endotracheal intubation. Due to proximity of the patient, infection could also spread by touch or conjunctival contamination. It is also possible to have faecal transmission during colonoscopy. COVID-19 has significantly impacted endoscopic practice in India, as it has in the rest of the world. International guidelines are hard to follow in a country like India with limited resources, including limited PPE, lack of negative pressure units, overcrowding of centers, and limited resources in privately owned or smaller endoscopy units. Current recommendations to avoid endoscopy in elective cases are being followed by endoscopists. Adoption of international guidelines to tailor to the specific practice environment in India is desirable, especially when endoscopy units are reopened or should we have another surge in the SARS-CoV-2 infection.
There is, however, a more positive outlook into 2021, as market expects to move toward normal and endoscopy procedures restart.











