Molecular Diagnostics
HBV, HCV, HIV, and TB Drive Clinical Molecular Diagnostics
HBV,HCV, HIV, and TB with a combined contribution of 78 percent dominate the clinical molecular diagnostics segment. This is expected to continue till TB is eradicated in India by 2025 and viral hepatitis by 2030.
Molecular diagnostics has emerged dramatically over the last two decades, as advanced technologies have driven this industry toward the next level of significance. Companies that have already adopted molecular diagnostic methods are now benefitted by increased accuracy and improved sensitivities in their tests compared to others. These new methods have greatly enhanced the discovery of many microbial infections, as well as genetic illnesses. Those who were hesitating due to the challenges and expense of opening a molecular lab now run the risk of being at a competitive disadvantage. Molecular diagnostics has paved way for collaboration among many companies to add up their strengths. Through the collaboration, they intend to strengthen their hold in the molecular diagnostic market and develop an integrated clinical-workflow solution and provide mass access to molecular diagnostics. Tie-ups with companies from other domains are mainly aimed at marketing of diagnostic tests. Only a handful of companies control more than two-thirds or more of the market for molecular tests. Companies like Roche will continue to lead the product portfolio that includes molecular diagnostic tests for oncology, virology, microbiology, and blood screening. Multiple insurance providers are associated with them as payers of high-end medical tests.
Today, companies aim to provide precision medicine with molecular testing solutions. The detection of common infectious diseases and the monitoring of treatment efficacy through specific assays and selection of individualized treatment options is now easier. Advanced products come with the capability to detect viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites simultaneously. Real-time PCR products are user-friendly and operate with one step.
 Sudip Banerjee
Sudip Banerjee
National Sales Manager,
Qiagen lndia“For next-generation sequencing applications, Qiagen has launched the NGS GeneReader system. The platform redefines the NGS workflow by providing unmatched batching flexibility with multiple flow cells (1-3). Its inventive turntable design makes it possible to sequence multiple samples (up to 42 samples at a time) independently and in a parallel or staggered manner. The platform is now available for use with an expanded targeted gene panel menu, including the GeneRead QIAact actionable insights tumor, BRCA 1/2, and lung DNA panels, covering copy number variants (CNVs), SNVs, and indel variants, to provide deeper cancer research insights than ever before. This system has been launched in India in 2019. The first true diagnostics based NGS platform, it is going to revolutionize the way sample testing is done in the country, with the first installation in progress and two more in the pipeline”.
 Indian market dynamics
Indian market dynamics
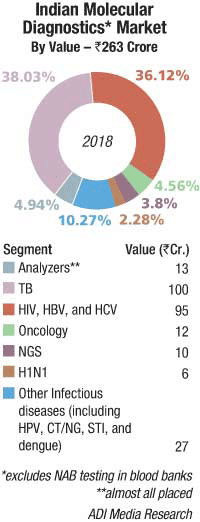
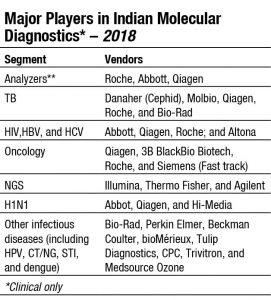
The Indian molecular diagnostics market is estimated at Rs 263 crore in 2018. Analyzers contributed Rs 13 crore, and most were placed. Roche, Abbott, and Qiagen continue to be the three dominant vendors.
In the reagents segment, TB at Rs 100 crore and HIV, HBV (hepatitis B virus), and HCV (hepatitis B virus) at Rs 95 crore have a combined contribution of 78 percent. India has set itself an ambitious target of eradicating tuberculosis by 2025. The large-scale implementation of the Indian government’s Revised National TB Control Program (RNTCP) is largely responsible for TB testing. There is not so much testing done by the private labs, and easy-to-use home kits are also available at very competitive prices.
Diagnosis of TB has entered an era of molecular detection that provides faster and more cost-effective methods to diagnose and confirm drug resistance in TB cases; meanwhile, diagnosis by conventional culture systems requires several weeks. New advances in the molecular detection of TB, including the faster and simpler nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS), have resulted in a shorter time for diagnosis and, therefore, faster TB treatments.
Danaher (Cephid) has a very large share in the Indian TB testing segment. The TrueNat test developed by MolBio Diagnostics can diagnose TB in one hour, as well as testing for resistance to the drug rifampicin. In 2016, six TB-related MolBio diagnostic products received CE-IVD marking. In January 2019, Qiagen announced plans to develop a proprietary new version of a QuantiFERON-based tuberculosis (TB) test, dedicated and tailored to the needs of low-resource regions, with a high disease burden of TB like India. The new testing solution, QuantiFERON-TB Access (QFT Access), is designed to pair ultrasensitive digital detection of latent TB infection with a complete workflow created with a focus on cost efficiency and ease of use. Clinical trials are planned to start in 2019, and commercialization is expected to begin in 2020. In May 2019, Roche announced the CE-IVD launch of the cobas MTB-RIF/INH test to detect resistance to antibiotics within the tuberculosis DNA.
 The National Viral Hepatitis Control Program was launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India, on the occasion of the World Hepatitis Day, July 28, 2018. It is an integrated initiative for the prevention and control of viral hepatitis in India to achieve Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.3 which aims to ending viral hepatitis by 2030. This is a comprehensive plan covering the entire gamut from Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, and the whole range from prevention, detection, and treatment to mapping treatment outcomes.
The National Viral Hepatitis Control Program was launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India, on the occasion of the World Hepatitis Day, July 28, 2018. It is an integrated initiative for the prevention and control of viral hepatitis in India to achieve Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.3 which aims to ending viral hepatitis by 2030. This is a comprehensive plan covering the entire gamut from Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, and the whole range from prevention, detection, and treatment to mapping treatment outcomes.
In May 2019, Abbott announced that m-PIMA HIV-1/2 VL, the world’s first point-of-care viral-load diagnostic test, received the World Health Organization’s prequalification approval (WHO PQ). The test had received CE mark in December 2018. To provide the most effective HIV treatment and care, the WHO has recommended that everyone receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) undergoes a viral-load test at 6 months and 12 months, and annually thereafter, if the individual is stable on ART.
It is estimated that in 2018, the Indian market for oncology, NGS, and H1N1 tests was Rs 28 crore. Other infectious diseases as HPV, CT/NG, STI, and dengue are also increasingly being diagnosed by molecular methods.
Global market
The global molecular diagnostics market is expected to reach USD 19.8 billion by 2026 with an increase in CAGR of 9.1 percent during 2018 to 2026, predicts Grand View Research Inc.
In 2018, reagents was the largest revenue-generating segment with their elevated usage rates. Infectious diseases dominated the overall molecular diagnostics market in 2018. The oncology application segment is expected to exhibit a CAGR of around 11.8 percent over the next 8 years with rising awareness among people as well as healthcare professionals, pertaining to cancer diagnosis. PCR segment is expected to dominate the market in near future with increased use of PCR in genomics and proteomics research and rapid advancements and automation of the PCR technology. In 2018, hospitals dominated the end-user segment owing to the increase in the number of diagnostic tests conducted in hospitals.
Vendor updates
In August 2019, OTraces Inc. has completed the preliminary study regarding the detection of pancreatic cancer. The company used biomarkers for pancreatic cancer that were selected from a survey of relevant proteins that are active in the tumor microenvironment (TME).
In June 2019, BD has launched the CE-IVDD certification of the BD COR system in Europe. This system acts as a solution for diagnosing infectious diseases that set a new standard in automation for molecular testing in core laboratories and other centralized molecular laboratories.
Way forward
A common theme for healthcare in the coming years will be high efficiency through automated and easy-to-handle techniques combined with optimized sample preparation. Large research-based hospitals have already begun integrating molecular testing methods into their clinical labs with advanced processes. Technology has made new molecular diagnostic methods faster and less complex. Some of these tests are now automated and commercially available at low cost. Even smaller labs are trying to acquire molecular capabilities with advanced technologies because they can benefit from simpler, easier-to-use, labor-saving systems. The powerful tools and more accurate detection of disease are giving the laboratories a key role in the emerging field of personalized medicine. Molecular diagnostics capability is set to become a game changer for clinical laboratories.
Industry Speak
Molecular diagnostics – A leap in clinical technology
 Nitin Sawant
Nitin Sawant
President,
Trivitron HealthcareRecent advancements in sub-cellular molecular technology is a prime factor in framing our approach to diagnosis and therapy for a wide range of maladies. Molecular diagnostics includes a series of advanced and complex procedures for the analysis of biomolecules like DNA and RNA in a tissue or fluid. This enables to establish the identity of the causative infectious organism or reveal the underlying genetic makeup of the patient exhibiting certain phenotype.With the recent advancement in molecular diagnostics, knowledge of the genetic composition of the subject enables identification of risk of a disease or assess the effectiveness of a particular treatment regimen, most suitable for a particular disease. As a tool for genetic screening, the molecular diagnostic tests enable patients to understand risk of occurrence of specific condition before the onset of the same.Molecular diagnostics is involved in a variety of hereditary and genetic tests that keep on evolving day by day. Few of the most advanced genomic analyses relying heavily on molecular diagnostics include:
Gene mapping. Molecular diagnostics finds a great deal of application in the human gene mapping process where extensive research is being carried out to construct a detailed genetic map of the human genome and determine the entire sequence of DNA.
Real-time PCR. Also known as quantitative PCR, is a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based laboratory technique of molecular biology that combines PCR amplification and detection in a single step thus giving results in a shorter duration of time.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS). One of the latest entrants in DNA sequencing technology, this method of molecular diagnostics has actually revolutionized genetic research. NGS has emerged as a powerful platform that enables the simultaneous sequencing of millions of DNA molecules. NGS is a high-throughput option with capability to sequence multiple individuals at the same time.
Personalized medicine. A relatively futuristic technology wherein by utilizing molecular diagnostics, medical treatment is tailored according to individual characteristics of each patient. Therapeutic approaches are being developed keeping in mind the genetic make-up of the patient so that precise treatment is administered.
Molecular diagnostics in true sense is a transformative technology with revolutionary offerings; however, it faces certain challenges like lack of proper regulatory policies, data archiving tools, high costs, data secrecy, and others. However, a multitude of molecular techniques are now being utilized in the clinical field, hence making it an integral part of clinical practice. Agreed, there are a few challenges, but with the day-by-day advancement in technology, those challenges can surely be overcome.
Perspective
Throw that tourniquet away
 Dr DM Vasudevan
Dr DM Vasudevan
Technical Director,
Agappe Diagnostics Ltd.T he pre-analytical phase accounts for majority of errors made in a laboratory test result, with a reported error rate of 60–75 percent. A case of decreased vein visibility is a nightmare for phlebotomists as well as for the patients. This often decreases the perceived efficiency of the laboratory by the patient during the sample collection process itself and lowers the patient satisfaction also.Vein detectors are medical devices that make use of a particular technology that aid healthcare providers by increasing visibility of veins for a successful venepuncture procedure. The usage of vein detectors is especially helpful in elderly, dark-skinned, obese, agitated or restless, and oncology patients undergoing chemotherapy. Various complications such as hematoma, infections, nerve damage, extravasations, excessive bleeding, edema, thrombosis, and allergies may arise as a result of venepuncture complications. Increased efficiency, ease of procedure, and accuracy are some of the factors that are in favor of the vein detectors.At Agappe, we strive to bring innovations into the Indian IVD industry. We have simplified the pre-analytical process of sample collection with a new solution. We proudly present, to every phlebotomist and physician in the nation, a product from the joint venture between Sree Chithra Thirunal Institute of Medical Science and Technology and Agappe Diagnostics Ltd., a perfect collaboration of the technical know-how from the Institute and the manufacturing capabilities of the largest Indian IVD manufacturer.
The Mispa View is incorporated with infrared vein-finding technology, which removes the guess work out of the conventional method of visual checking and utilizes accurate visualization, thereby improving patient satisfaction.
A complete portable device, providing hands-free operation, Mispa View can provide a high-quality image on display with its 5 MP infrared camera at a wavelength of 850nm. 6× zooming and automatic brightness adjustments give the best visibility compared to other projection-based devices. Added intensity-adjustment features and different color displays improve the easiness to view the veins without the interference of ambient lighting. A perfect zero-downtime equipment with rechargeable Li-ion battery with a backup of above 3 hours, Mispa View can be used to view veins at any angle. It uses low IR radiations visualizing veins up to 3 mm deep. This low radiation makes Mispa View safe to be used even on pregnant ladies.
Hematology technologies are moving toward more clinical-decision support
 Nitin Srivastava
Nitin Srivastava
National Sales Manager,
Head – IVD Sales and Marketing,
Nihon Kohden India Pvt. Ltd.H ematology technologies are moving toward more clinical-decision support, where analyzers are capable of providing decision support reports and tools to physicians/clinicians, enabling creation of correct investigation pathways and care protocols. Flagging for abnormal result is a growing demand where pathologist wants to have customized indicative flagging feature for abnormal cells.Market demands to reduce the size, cost effectiveness, low maintenance, and reliable date, linearity of the parameter, reproducibility, and accuracy by unique hardware design of the instrument.Data management software for hematology instruments is also a key feature of the product. It interprets and carries out the orders of the instrument operator. It gives a clear colored histogram and scatter gram, which is different for every customer and depends on the measurement techniques and parameters measured by the analyzer. The graphical presentation enriches the user experience and helps to reduce operator error.
India has been one of the growing healthcare markets, and when it comes to hematology instruments and reagents, it is expected to grow 12 to14 percent per year. The market will grow along with the development of medical system in India. With an increase in awareness about diagnostic tests and a manifold increase in the index of infectious diseases in the country, it has turned out to be a favorable market-growth situation.
Hematology instruments and reagents continue to maintain strong position globally and the hematology market globally is expected to reach USD 4.5 billion by 2020.
Over the years, hematology instruments have evolved from simple manual red blood cell counters to sophisticated automated analyzers. Nowadays, it is difficult to find semi-automatic hematology analyzers as they have been already replaced by fully automated analyzers in developed countries. The trend is about to follow in Tier-III Indian market also.
The analytical automation systems simplify testing process, reduce manual work, and further increase the efficiency and productivity of laboratories.
Reliability of data is one of the key concerns for users. The main factors to secure data reliability are maintenance of instruments, qualified genuine reagents, and daily QC programs using hematology controls. Companies that can provide these factors can dominate with a considerable growth in the market.














