MB Stories
Improving disease management and therapy with MDx

Over the next seven years, the molecular diagnostics market is poised for a magnificent spike in CAGR in terms of revenue.
Molecular diagnostics has emerged as a viable and cost-effective alternative for infectious disease testing, particularly in resource-limited environments with diverse potential causes of infection. Their rapidity, complexity, and adaptability make them highly valuable, allowing healthcare systems to optimize resources and respond promptly to emerging risks.
While several diagnostic methods, such as antigen and antibody detection, morphological identification, smear microscopic examination, nucleic acid detection, and microbial culture, are widely used, they have inherent limitations. These include a restricted range of detectable pathogens, low sensitivity, and prolonged detection cycles, which pose challenges in identifying infections caused by rare or novel pathogens.
To overcome these limitations, ongoing advancements in genetic and genomic studies have facilitated the rapid and sensitive identification of infectious diseases, using nucleic acid detection-focused molecular diagnostic tools. Techniques, such as high-throughput sequencing, polymerase chain reaction, gene chip technology, and isothermal amplification reaction, are widely employed as primary diagnostic methods.
Advances in molecular diagnostics
 Dr Manoj Chugh
Dr Manoj Chugh
Vice President, R&D (Reagents),
Transasia Bio-Medicals Ltd.
Molecular diagnostics is evolving at an incredible pace.
Molecular diagnostics has been largely influenced by the proliferation of infectious diseases, and chronic illnesses, including cancer and heart diseases. Automated systems for extraction, DNA/RNA amplification, their detection using labels have propelled the rapid development of molecular technology. This has led to an expansion of diagnostics using DNA or RNA analysis in clinical laboratories. Further, the discovery of additional biomarkers will aid in the accurate and timely diagnosis of a patient as well as the prediction of the patient’s response to therapy.
Techniques for testing genetic materials
Current technologies for analyzing genomic aberrations in clinical applications include real-time PCR (qPCR), fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), microarrays, and next-generation sequencing (NGS). These cutting-edge methods present a chance to deliver rapid diagnosis by achieving ultra-high sensitivity.
Real-time PCR is rapidly replacing traditional microbial detection methods as it not only detects infection but also the drug resistance status of the pathogen, which provides an immediate treatment plan with effective drugs, reduces the generation of drug-resistant pathogens, and facilitates the recovery of patients. Similarly, real-time PCR is also used for mutation detection (BCR-ABL1, PML-RARA, EGFR, KRAS, etc.) and for monitoring the drug response in cancer diagnosis and treatment.
In cancer prediction and early detection, specific germline mutations like BRCA1 and BRCA2, TP53, gene rearrangements, etc., can be detected using NGS. Cancer screening using NGS has contributed to decreasing the morbidity and mortality of cancer; therefore, molecular diagnostics not only detects but also categorizes the types of diseases, helps clinicians make more informed treatment choices, and also helps them predict the outcome of treatment.
What the future holds
Technological advancements have led to the creation of molecular POCT devices that are capable of on-site, real-time testing, allowing for rapid diagnosis and treatment choices. PCR-based testing outweighs all alternatives, as sequencing devices are more expensive, other technologies aimed at examining genome complexity without PCR are expected to gain traction in the coming years. The notion of traditional wet lab will evolve to lab-on-a-chip with the advent of integrated silicon chips loaded with biomolecules, that can analyze hundreds of genes/proteins in hours.
These molecular diagnostics have become essential for the early diagnosis of infectious diseases, allowing for the detection of multiple pathogens, analysis of drug-resistant genes, and pathogen homology assessments.
Molecular diagnostics in infectious diseases encompass testing the host’s susceptibility to disease, screening for infections, diagnosing key infections, and tracking disease progression and pathogen spread. These tests are highly sensitive and specialized, reducing the need for unnecessary diagnostic procedures, medications, and hospital-acquired infections. Molecular testing improves patient care and offers potential financial benefits by optimizing resource utilization and reducing healthcare costs.
Overcoming challenges and embracing advancements in molecular diagnostics will continue to be instrumental in the effective management and prevention of future outbreaks. By leveraging the power of molecular technologies, healthcare systems can proactively protect communities, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately preserve and improve global public health.
Indian market dynamics
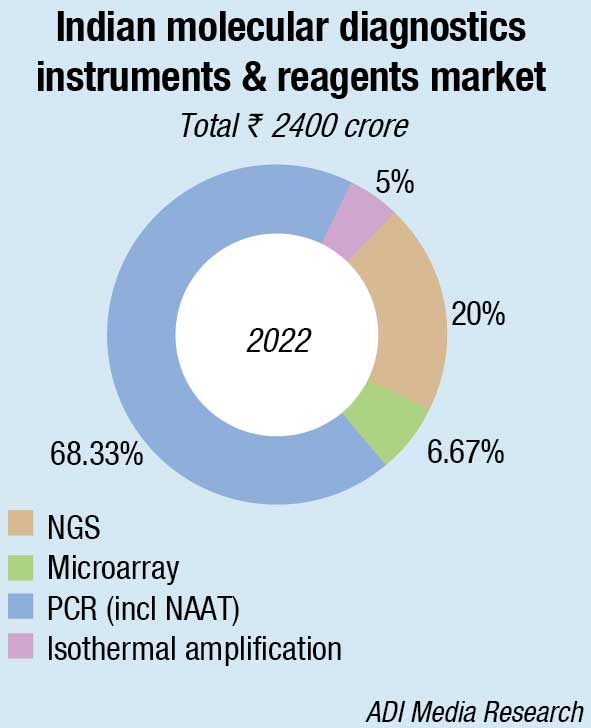
The Indian molecular diagnostics instruments and reagents market in 2022 is estimated at ₹2400 crore, and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 7 percent until 2026. In 2022, the reagents segment dominated the Indian market with a revenue share of 65.38 percent. By technology, the PCR segment dominated the infectious disease molecular diagnostics market and accounted for 68 percent share. NGS commands a 20-percent market share, with the balance being from microarray and isothermal amplification.
By application, infectious disease held the largest market share of 96.5 percent. The oncology segment was also one of the major market shareholders.
The point-of-care segment is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 11.61 percent over the next five years, owing to an increase in the demand for bedside testing, the need for accurate results, and a rise in awareness about healthcare.
|
Leading players -Indian molecular diagnostics instruments & reagents market |
|
| Tier 1 | Thermo Fisher, Roche, Illumina, Qiagen, and Cepheid. |
| Tier 2 | Snibe, TRUPCR, Bio rad, bioMérieux, HiMedia, Molbio, Abbott, and Mylab. |
| Tier 3 | Genes2me, Agappe, Siemens, Randox, Zybio, and MGI. |
| Others | BD, Transasia, Agilent, Helini, Tata MD, Solution One, Angstrom, and ACON. |
| ADI Media Research | |
There’s something in the air
 Jason Armstrong
Jason Armstrong
Scientific Content Creator,
Randox Laboratories Ltd
It’s that time of year again. The chill in the air is returning, indicating not just the beginning of winter but also the arrival of flu season. Queue the sniffles, sneezes, and shivers. But this year, there is something else in the air – a sense of preparedness.
At Qnostics, we are arming you with the tools you need to ready yourself for the influx of infectious disease testing by providing true third-party, whole-pathogen quality controls.
WHO estimates that influenza epidemics result in 3–5 million severe illnesses annually and up to 650,000 respiratory deaths.
If we have learned one thing in recent years, it is how quickly viruses can spread and infect large populations, providing a reminder of how important infectious disease testing is; by identifying those infected, we can take steps to limit the spread of the virus. While these viruses are normally self-limiting in healthy adults, they can have severe consequences for the elderly and the immunosuppressed.
The landscape of infectious viruses is dynamic, but one thing remains constant – the need for accuracy and reliability in diagnostic testing. At Randox, we understand the vital role molecular controls play in ensuring your results are as precise as possible. That is why we are excited to showcase the Qnostics range, your ultimate ally in conquering viruses like Influenza A and B, RSV, adenovirus, rhinovirus, and beyond. With Qnostics, you are not just testing; you are safeguarding health with confidence.
Our range of Q controls provides an independent and unbiased assessment of assay performance while helping maintain your ISO15189:2022 accreditation. Traceable to international reference materials, our whole-pathogen controls are designed to mimic the performance of patient samples, testing all stages of the molecular process – extraction, amplification, and detection.
But that is not all. In addition to our Q controls, the Qnostics range includes evaluation panels for verification and validation, analytical Q panels for assessing linearity, LOD and LOQ, and molecular Q panels to help laboratories evaluate the analytical performance of your molecular assays.
Discover how Qnostics can revolutionize your molecular quality control procedures by visiting: www.randox.com or contacting us at [email protected].
With Randox, you are not just prepared for flu season; you are leading the way in infectious disease diagnostics with the full support of a trusted partner.
The molecular diagnostics market in India is at an exciting juncture, driven by growing interest from investors, corporates, and startups. September 2022 saw Singapore-based investment firm Temasek invest USD 85 million in Goa-based diagnostics chain, Molbio Diagnostics Pvt. Ltd. In August 2022, Novo Holdings A/S had led a USD 50 million investment into MedGenome, a leading genetic diagnostics, research, and data company, alongside its existing investors, LeapFrog Investments and Sofina. Corporates like Reliance Industries and Tata Group, and startups like D-nome and Swagene, are increasingly getting active in this segment.
Emerging application areas of molecular diagnostics include genetics, hematopathology, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological diseases. India currently has 3000+ molecular testing laboratories.
Advancements in molecular detection – Opportunities and challenges
 Prof. Praveen Sharma
Prof. Praveen Sharma
Scientific Consultant,
Snibe India
The Indian market for molecular diagnostics is expanding at an unprecedented rate, driven by the pandemic of Covid-19, increasing awareness about personalized medicine, and the government’s focus on affordable healthcare and initiatives to promote manufacturing from indigenous to transnational.
The Indian molecular diagnostics industry is witnessing remarkable advancements in technology, thanks to the competition among various manufacturers, and the government’s support. To meet the high-volume demand of clinical diagnosis needs, the most attention has been paid to the integrated PCR analyzer, which simplifies the complex operation of traditional PCR in pretreatment. The analyzer runs the whole diagnostic process automatically, saving manpower and shortening the operation time.
Digital PCR is emerging as a powerful tool for laboratory diagnostics, with the latest example being the Molecision S6. It integrates droplet generation, PCR amplification, four-color fluorescence detection, and data analysis. It simplifies the complex process of traditional PCR and quantitative results.
The next-generation sequencing (NGS) allows simultaneous analysis of multiple genes, and offers valuable insights into disease pathology. This technology has the potential to revolutionize diagnostics by enabling precise diagnosis, treatment selection, and monitoring of disease progression. And the microarrays, and mass spectrometry-based methods are gaining popularity due to their high sensitivity, specificity, and throughput capabilities.
Moreover, the field of molecular diagnostics is experiencing a paradigm shift toward point-of-care testing (POCT), with miniaturized devices, such as handheld PCR machines and biosensors becoming increasingly prevalent in resource-limited settings. These technological advancements are crucial in addressing healthcare challenges in rural areas and enhancing patient access to timely and accurate diagnostics.
While the molecular diagnostics industry is making strides, it still faces certain challenges that need to be addressed, including regulatory complexities and lack of standardization. However, these challenges also present immense opportunities for collaboration among key stakeholders, including IVD manufacturers, government, and academia to develop robust regulatory frameworks, establish quality standards, facilitate knowledge sharing, and promote fair business competition relationships.
It is the responsibility of all healthcare industries to bring affordable and secure healthcare to people all over the world. The field of IVD in India, even around the world, is expected to develop rapidly in the near future.
Fruitful collaborations in MDx
Collaboration among companies in the field of molecular diagnostics can be highly beneficial in several ways, contributing to advancements in technology, research, and the overall impact of molecular diagnostics on healthcare. Collaborations are helpful in resource sharing and accelerated innovations can lead to the development of new diagnostic techniques, assays, and technologies.
Collaboration allows companies to share the financial burden, making it more feasible to bring new tests to market and help companies to expand their market. It enhances the ability to address complex healthcare challenges and deliver more effective diagnostic solutions to benefit patients and healthcare systems. Some of the collaborations in the pipeline in India include:
- TechInvention Lifecare Pvt. Ltd., a Mumbai-based biotech start-up collaborating with Reagent IVD Resources Pvt. Ltd. (RIVDR), a Jaipur-based diagnostics, to focus on the development and manufacturing of a comprehensive range of diagnostics.
- Xume, India’s first artificial intelligence (AI)-powered grocery scoring and recommendation platform, has taken a huge leap forward by joining forces with Microbiome.in and TruDiagno. They aim to empower individuals to make informed choices, based on the state of one’s gut microbiome and key diagnostic markers, propelling preventive healthcare to a new level.
- Molbio Diagnostics, based in Goa, has collaborated with SigTuple to build next-gen diagnostic testing devices. The aim of the partnership is to bridge this gap and enable most basic tests to be performed in near-patient settings. Both companies are collaborating on the development of AI-powered, battery-operated, portable devices for many diagnostic tests in the fields of hematology, biochemistry, electrochemistry, and others.
- There is one collaboration worldwide among The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria (the Global Fund), the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), and the Stop TB Partnership with Molbio Diagnostics that significantly reduces the price of the Truenat® MTB and MTB Plus tests. This collaboration will expand equitable access to quality rapid testing to underserved populations across all countries.
Recent developments
- Hyderabad-based molecular diagnostics start-up D-nome raised investment from Ankur Capital in 2022.
- Genetic Analysis, a molecular diagnostic specialist, partnered with Mumbai-based Microbiome Research Pvt. Ltd. to launch GA-map technology in India in 2022.
- The Tata Medical and Diagnostics is an emerging player in the molecular diagnostics market. It is developing molecular diagnostic solutions for infectious diseases and cancer.
Reliance Industries plans to roll-out a comprehensive and affordable genome sequencing kit, developed by Strand Life Sciences.
Mergers and acquisitions
Molecular diagnostics companies have been the subject of much M&A activity in recent years, which has helped to expand and evolve the capabilities of larger companies in areas, such as in vitro diagnostics and precision medicine.
After hitting an unprecedented height in 2021, mergers and acquisitions in the omics tools and molecular diagnostics space returned to a more normal level in 2022. Deal volume fell by roughly half year-over-year, with 51 total deals notched in 2022, compared to 101 in 2021. For comparison, the space saw 53 deals in 2020 and 62 in 2019. Values of deals were disclosed for 18 of the 51 deals in 2022, totaling USD 7.85 billion.
2022 was marked by deals, including Bio-Rad’s acquisition of Curiosity Diagnostics for USD 170 million and BD entering an agreement to acquire Spain-based Cytognos. Investors are also retaining their sights on the molecular diagnostics market across all fundraising stages, with Synthego, TauRx Therapeutics, and Scipher Medicine – all examples of companies that have garnered significant investment in 2022.
A trend has emerged where companies are now favoring private equity investment instead of following the route of IPOs and SPAC mergers. According to Biotechgate data, only one molecular diagnostics organization went public in 2022 – Virax Biolabs, who held their IPO in July. Following this, their price on the Nasdaq has plummeted.
In October 2022, Thermo Fisher announced that it was acquiring the Binding Site Group from a group of equity investors for USD 2.6 billion from private equity investors. Under the agreement, Thermo Fisher gained access to Freelite, a diagnostic testing solution for the diagnostic treatment and monitoring of multiple myeloma across all stages of the disease that has been recommended by leading publications. The deal also brought a range of diagnostic assays for other blood and immune system disorders.
SD Biosensor, along with private equity firm SJL Partners, in July 2022, led a consortium to purchase the diagnostic solutions and life sciences raw materials company Meridian Bioscience for USD 1.5 billion. The deal was originally scheduled to close by the end of 2022 but was postponed until the end of January 2023. SD Biosensor owns 60 percent and the remaining 40 percent is owned by SJL Partners. Cincinnati-based Meridian Bioscience continues to operate independently. By buying Meridian, SD Biosensor gained an entry into the US in vitro diagnostics market.
In April 2022, Finnish business Medix Biochemica acquired myPOLS Biotec, which will continue with its operations in Konstanz, Germany. Forming a significant part of the newly established molecular diagnostics business unit within the parent group, all founders of myPOLS Biotec remain involved in the business.
And recently, in July 2023, New Day Diagnostics LLC announced it has entered into an agreement to acquire the assets of Epigenomics AG, a molecular diagnostics company focused on blood testing for the early detection of cancer. The acquisition would expand New Day Diagnostics’ portfolio in the cancer diagnostics space and include proprietary biomarker technology for the detection of methylated DNA in various cancer indications, including Epi proColon, a screening tool for the non-invasive detection of colorectal cancer.
In the same month, Yourgene Health, a Manchester, England-based molecular diagnostics group, reached a definitive agreement to be acquired by Novacyt for GBP 16.7 million. The acquisition strongly aligns with Novacyt’s post-Covid strategy, which includes pursuing strategic mergers and acquisitions to support its long-term growth and prioritized the twin objectives of geographic expansion and portfolio development.
Global market scenario
Molecular diagnostics has undergone a period of rapid development and growth in the last decade. Growing demand for reliable early-stage diagnosis of chronic ailments is likely to add impetus to molecular diagnostics (MDx) market growth in the coming years. This growth is largely characterized by prolific technological advancements and the subsequent development of sophisticated molecular diagnosis techniques.
Traditional diagnostic techniques include microbial culture, hemagglutination inhibition tests, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). Of these, the culture of pathogenic microorganisms is the most time-consuming and their identification is mainly based on morphological characteristics, with low specificity and sensitivity.
In addition, immunological methods, such as hemagglutination inhibition assays and ELISAs, used for the detection of pathogen-specific antibodies or antigens, are simple to perform; however, they have disadvantages such as high false-positives, high cost, and poor thermal stability.
With the continuous development of genetic and genomic research, molecular diagnostic techniques focused on nucleic acid detection have provided new methods for the diagnosis of infectious diseases, with a short turnaround time and high sensitivity.
Exercising ‘One Health’ – Providing effective solutions to combat AMR
 Dr. Kavita Khadke
Dr. Kavita Khadke
D.P.B, MD (Pathology), Director – Molecular Biology,
HiMedia Labs Pvt.Ltd.
The Indian molecular diagnostics industry has witnessed an immense growth and technological advancements in recent years, with Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) emerging as a key area of focus. The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India published the National Action Plan for containing Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in April 2017, describing the strategic implementations for disciplining AMR.
Misuse and overuse of antibiotics and other antimicrobials have led to development and spread of drug resistant bacteria and thus poses a significant global threat. Additionally, the interdependency in the life cycle of humans, animals and environment have also been playing a cumulative role in the rise of AMR. The One Health approach is a considerable step taken by WHO for combating this risk.
Encouraging the welfare of Human, Animal and Environmental Health and aiding in fighting back the resistant organisms, HiMedia® – HiGenoMB® has aggregated a complete automated solution for AMR panel as a diagnostic solution.
The panel is inclusive of magnetic bead-based automated nucleic acid extractor/kits , followed by real-time PCR system/kits for targeted amplification to detect the presence of resistance genes and to check for specific mutations by sequencing.
HiPurA® automated nucleic acid purification kit (MB583 series) is a multi-sample extraction kit. Blood, plasma, serum, saliva, buccal swab, tissue, urine and cells, are the specimens which can be used for extraction of nucleic acids. With pre-filled plates/cartridges, the kit saves time, reduces reagent wastage and increases efficiency.
Hi-PCR® AMR panel is an assembly of multiplex probe-based detection/quantification kits of five commonly known drug resistant genes. MBPCR131 – β-lactamases gene, MBPCR132 – carbapenemase gene, MBPCR133 – methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus, MPBCR134 – vancomycin resistant enterococci and MPCR209 – colistin resistance.
Combined with our Hi-Gx360® sequencing and bioinformatics services for whole genome sequencing (MBS201) one can also identify and comprehensively profile all AMR associated genes using (MBS011) bioinformatics services.
HiMedia® – HiGenoMB® always aims at working hand-in-hand with the healthcare industry, assisting and aiding throughout the drive for curbing threats, and working towards finding solutions for evolving challenges.
Molecular diagnostic techniques can not only detect multiple pathogens, but can also analyze drug-resistance genes of pathogens and pathogen homology analysis, and have gradually become an important tool in the early diagnosis of infectious diseases.
At present, the commonly used molecular diagnostic techniques for infectious diseases include PCR, isothermal amplification reaction, gene chip technology, and high-throughput sequencing technology.
In addition to rising research and development efforts, the rising prevalence of infectious diseases worldwide, alongside rising demand for point-of-care (POC) diagnostic solutions are some more factors that will add further impetus to molecular diagnostics industry demand over the years ahead.
Market dynamics
The global molecular diagnostics market is projected to reach USD 27 billion by 2030 from USD 13.6 billion in 2022, at a CAGR of 9.0 percent. Rising requirement for cancer diagnosis and development of precision medicine are majorly growing market revenue.
Moreover, patients often prefer non-invasive or minimally invasive procedures as they are less painful, have shorter recovery times, and reduce the risk of complications, leading to rising demand for the molecular diagnostics market.
Reagents and kits contributed to the largest market share and reached USD 16 billion in the year 2022. The frequent requirement of reagents and kits is a significant factor contributing to the market’s growth.
Furthermore, technological advancements in molecular diagnostics continuously drive the development of new and improved reagents and kits. The availability of advanced reagents and kits that offer enhanced performance and reliability fosters their widespread adoption, and contributes to the segment’s growth.
By test type, lab tests segment held the largest share in the market. The growing demand for automation in laboratory settings and the increasing incidence of various infectious diseases are fueling this segment. Lab tests have superior sensitivity and specificity compared to PoC tests due to the controlled environment, minimizing false results. This precision is vital for infectious diseases diagnosis and containment. Labs also offer high sample throughput, thanks to automation, driving segment growth.
The hospitals segment exhibits more than 3.5 percent CAGR. This is due to the growing disease burden and the emergence of novel epidemics and pandemics. And with the increased spending on healthcare infrastructure, the network of hospitals and clinics worldwide is set to expand significantly.
North America holds a major share in the market registering at a CAGR of 9.3 percent as there is more technological advancements in the field of molecular diagnostics, robust R&D infrastructure, which has led to the rapid adoption of innovative diagnostic techniques and platforms, although data safety challenges, presence of alternative testing methods, and stringent regulatory requirements act as barriers to hamper the market’s expansion.
The overall market for molecular diagnostics has made significant strides, empowering physicians to assess disease predisposition, implement precise diagnostics, and tailor individualized therapies for conditions like cancer and infectious diseases.
POC market
The point-of-care (POC) molecular diagnostics market is predicted to secure a valuation of USD 4.4 billion in 2023 and is rising to USD 11.1 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 9.7 percent.
The growing advanced technology, diagnostic tests, preventive medicine, and knowledge of molecular mechanisms are driving the market growth. The adoption of POC diagnostics by laboratory specialists for sequencing DNA and multi-gene are expanding the market size. These diagnostics rapidly show the results with accuracy. Increasing respiratory, gastrointestinal, and sexually transmitted diseases are advancing the market growth. Emerging economies, government initiatives, and low-cost POC molecular diagnostics are the prime factors that propel market opportunities.
The RT-PCR category dominates the global market with its remarkable CAGR of 9.2 percent during the ten year period 2022–2033. This is due to the rise in tests, such as genomics, Covid-19, proteomics, and others. It is a real-time system that shows results immediately, has high sensitivity, and is cost efficient.
Key players fragment the global market by contributing an impressive role. These players are bringing new ideas and adopting them to build advanced products, which in turn result in surging market opportunities. Growing technologies, including AI and the Internet of Things (IoT), have surpassed market growth in recent years.
By accepting these technologies, key players welcome better detection machines and equipment as per patients’ requirements. They further follow several effective marketing strategies, such as partnerships, mergers, acquisitions, agreements, and product launches.
Molecular technology has rapidly evolved
Automation in extraction, amplification, and detection, along with the emergence of next-generation sequencing, has led to an increase in clinical tests centered on DNA and RNA analysis. Clinical laboratories now employ technologies like real-time PCR (qPCR), fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), microarrays, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) to study genomic abnormalities for various clinical purposes.
Recent progress in molecular diagnostic technologies, giving new direction to healthcare with higher sensitivity and specificity, shorter detection time, and increased automation, performs an important role in the early and rapid detection of infectious disease pathogens.
MqPCR. Researchers have developed multiplex qPCR, which can simultaneously detect multiple pathogenic infections in a single sample using various sets of primers and probes, which reduces detection time, labor and reagent costs, and sample consumption.
Another recent study by Jiang et al. developed an MqPCR assay capable of concurrently detecting nine respiratory pathogens with no cross-reactivity and a limit of detection (LoD) of 250–500 copies/mL (1.25–2.5 copies/reaction), which is a promising alternative for the early screening of acute respiratory tract infections. This demonstrates the innovative multiplex real-time PCR assay as a promising alternative to the current approaches used for early screening of acute respiratory infections.
Third-generation sequencing (TGS). TGS has emerged as a breakthrough technology; it has shown great potential for screening and diagnostic applications in various diseases while its application in thalassemia detection is still in its infancy. TGS technologies mainly include single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing, nanopore sequencing, and synthetic long-read (SLR) sequencing.
Medical practitioners have started to recognize TGS as the preferred method over NGS due to detecting long deletion variants in the thalassemia gene, higher detection rates and diagnostic accuracy, and shorter turnaround time. However, it is not applied worldwide but it is anticipated that TGS will become a viable and cost-effective alternative for clinical laboratories to perform in-house thalassemia testing in the near future.
Biosensors. Advances in this technology will help in the establishment of bedside medical diagnostic devices. Five biosensors – electrochemical, optical, photoelectrochemical biosensors, piezoelectric biosensors, and aptasensors – are applied for the detection of tumor biomarkers. Electrochemical biosensors are helpful in early diagnosis, improving the treatment effect of patients, and improving the quality of life. Optical biosensors play an important role in clinical diagnostics and drug discovery, and also have the advantages of high sensitivity, good stability, and high reliability. However, there are still some challenges, which hinder their performance and need to be further improved, including reusability, stability, and compatibility with biological fluids. Furthermore, they should be more integrated, miniaturized, and portable in the future so that biosensors can be used to diagnose and manage cancer at a low cost in clinical laboratories and hospitals.
CRISPR-Cas technology. This system is a new generation of gene-editing technology that is commonly used for rapid molecular diagnosis and treatment. CRISPR-based diagnostics are easy to use, easy to carry, and take less time than the real-time PCR-based assay currently in use. CRISPR-Cas system has been shown to be useful in diagnosing and treating dengue, Zika, HIV, tuberculosis, and hepatitis B. DETECTR and SHERLOCK technologies based on CRISPR diagnosis are fast, effective, and low-cost.
DNA microarray chip. The newly designed biochip system, with species-specific 16S rRNA sequences for identifying 17 mycobacterial species, could be promising for diagnosing mycobacterial infections. DNA microarray biochip has simplified the procedure for nucleic acid extraction, convenient operation process, and concise interpretation of the result. This technology takes less time – around 6 hours – for results interpretation as compared to traditional culture methods and, therefore, shortens the diagnostic procedure. Each DNA microarray chip can simultaneously and rapidly test four samples, while each experiment can test 24 chips simultaneously.
This high-throughput feature reduces the need for repetitive work by the technician and the cost is very less compared to other molecular diagnostic methods. Thus, the DNA microarray biochip assay is a simple, rapid, high-throughput, and economical diagnostic detection method that is ideal for clinical screening of large numbers of samples.
Omics technologies. This includes genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, which are valuable tools for breast cancer research. These approaches provide insights into the molecular landscape of breast cancer, allowing for the identification of biomarkers and therapeutic targets that are pivotal in developing personalized treatment strategies. The potential benefit of the omics technologies in cancer research is vast, since they offer an unmatched opportunity to define cancer biology at many pathological and molecular levels.
Outlook
The dynamic landscape of molecular diagnostics is ushering in a new era of healthcare, characterized by personalized, precise, and efficient disease management. From the rapid evolution of nanobiosensors to the integration of multi-omics technologies, the future holds immense promise for early disease detection and tailored therapeutic interventions. India’s burgeoning molecular diagnostics market underscores its potential to transform healthcare accessibility. Globally, the field is poised for remarkable growth, driven by the demand for precision medicine and non-invasive diagnostics. Collaborations among companies and organizations further amplify the impact of these advancements. As we journey into this future, molecular diagnostics stands as a beacon of hope, enhancing patient care and safeguarding public health.
Second Opinion:-
Molecular assays hold huge potential for future diagnostics.












