MB Stories
Standing at a crossroads

The stage is set for the Indian industry to be a global medical device powerhouse. Improvement in infrastructure and research and innovation are needed, so that the shift can take place from being a producer of low-end medical devices and consumables to manufacturing high-end devices.
India has the potential to evolve as a global medical device powerhouse. It however stands at a crossroads, either it can continue being a producer of low-end medical devices and consumables or it can develop and improve infrastructure to stimulate research and innovation required to manufacture high-end devices.
There is a strong focus on promoting self-reliance in medical device manufacturing, encouraging indigenous innovation, and ensuring accessibility and affordability of medical devices for all.
Going forward, collaboration between manufacturers, regulatory bodies, and healthcare providers will be key to developing products suitable for the Indian patient population. Advanced technologies such as IoT, 5G, Generative AI, and 3D printing among others will help manufacturers to identify patient points and customize innovative solutions.
The role of innovation cannot be undermined. In the Indian context, innovation in medical devices can be defined as one that identifies specific patient challenges and provides affordable and sustainable care solutions to patients using new products and techniques without compromising on quality. The sector faces an interesting dichotomy with growing demand for innovative and latest technologies on one hand and the need to make them affordable on the other. Innovative health technologies can help enhance the quality of healthcare delivery by reducing the overall healthcare cost, reducing hospital stays, and real-time diagnosis of medical conditions.
Additionally, the increase in patient population with noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) is driving the need for affordable care solutions.
Another factor driving the need for innovation is competition. The medical device sector is highly fragmented in India, with players focused on manufacturing low-priced high-volume devices where the competition is intense. Recent few years have seen a focus to help India transition from manufacturing consumables to high-end medical devices. The proposed New Drugs, Medical Devices, and Cosmetics Bill, 2022, the approval of the National Medical Device Policy (NMDP), the establishment of research institutes such as the National Institute for Medical Devices Education and Research (NIMER), and the launch of National Policy on R&D and Research and Innovation in Pharma-MedTech (PRIP) scheme, The National Research Foundation (NRF) Bill, Production Linked Incentives (PLI) scheme, Assistance to Medical Device Clusters for Common Facilities (AMD-CF), and promotion of medical device parks are some initiatives taken by the government to create a conducive ecosystem.
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is one of the oldest, globally recognized medical research institutes. It is the apex body for coordination, formulation, and promotion of R&D in the biomedical field. Along with 26 network institutes, ICMR is actively involved in the evaluation of new drugs and therapies for all diseases of national health priority along with neglected and regional ones. Similarly, the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP) plays a vital role in driving R&D in the medical device sector. In the recently launched policy for R&D and innovation, DoP plans to set up a high-level task force to review and track implementation of the policy.
Academic research institutions are an important pillar that supports and promotes R&D in the country. Private sector contributions are critical for India to move up the value chain investment from private players will play a key role in embedding a culture of R&D in the industry along with providing a platform for upskilling and creating avenues for partnerships and collaborations.
India houses more than 250 start-ups in the field of medical devices and allied technology. In recent years, start-ups have picked up momentum in domestic as well as international markets. Strong backing of venture capital (VC)/private equity (PE) has been an important catalyst in catapulting the growth of start-ups. Medical robotics, medical imaging, and AI-powered diagnostics are some of the prominent focus areas of Indian start-ups in the sector.
In the last few years, there has been a major focus on digital therapeutics and wellness solutions with diabetes and cardiovascular diseases being the prominent therapeutic areas. Investments in the sector picked up significantly, especially in the last three years and have continued a positive trajectory into 2024.
Healthcare innovation market in India, currently valued at ₹2.55 lakh crore is expected to double by FY28, reaching ₹5.11 lakh crore, according to a recent report by Bain & Company and HealthQuad. Healthcare innovation has almost doubled over the past three years from a baseline of ₹1.36 lakh crore in FY20.
Pegged at ₹1.53 lakh crore in FY23, India’s overall healthcare market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12 percent to ₹27.2 lakh crore by the same time. Healthcare innovation accounts for about 15 per cent of the overall healthcare market in India, of which around 55 percent is export-led.
Growth will not only stem from value engineering but also from business innovation, particularly in biotech, vaccines, and MedTech sectors. Substantial growth in health tech and pharma services, which would contribute to this expansion are expected.
There are four key segments in the healthcare innovation space-pharma services, which include contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO), contract research organization (CRO), pharma IT (apart from HealthTech, vaccines and biotech), and MedTech.
HealthTech has witnessed strong growth since 2020. It accounted for roughly 25 percent of the healthcare innovation market in FY23, having more than doubled from about ₹25500 crore in FY20 to ₹59500 crore in FY23. The HealthTech market is split equally between consumer-facing solutions (like telemedicine, e-pharmacy, e-diagnostics, and wellness) and enterprise-facing solutions (like B2B e-commerce and SaaS-based hospital, clinic, and pharmacy management solutions). The pandemic provided a significant growth impetus for consumer-facing segments.
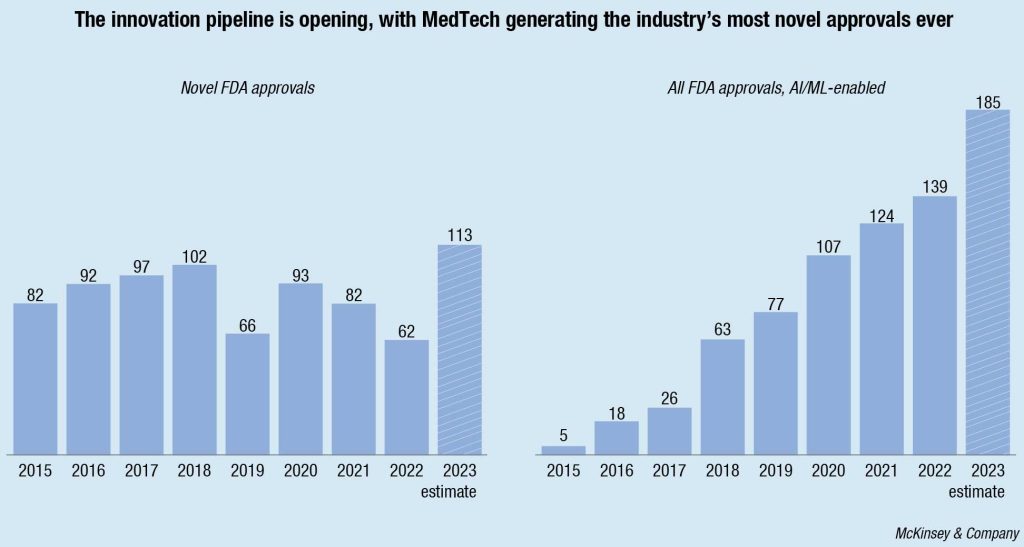
Globally, the industry is poised to deliver another banner year for innovation. In 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved more novel medical technologies than it has in any single year ever before. Several factors contributed: approvals of AI and machine-learning-enabled MedTech products reached an all-time high; miniaturization and improved visualization continued to drive approvals in cardiovascular and urology segments, among others; and digitally enabled categories, such as neuromodulation and robotics, continued to grow steadily. Also, waiting times for FDA reviews receded by almost 15 percent from 2020 to 2022.
Lawmakers and patients have called for scrutiny of the Food and Drug Administration’s medical device recall oversight after several high-profile recalls in the last five years. The U.S. Government Accountability Office said in January it would look into the agency’s oversight of medical device recalls, a little over a decade after a previous investigation by the watchdog found the FDA often failed to conduct recall-related inspections and document why a recall was terminated.
Recent safety problems with devices have gotten lawmakers’ attention again. Philips is still resolving a recall of more than 15 million sleep apnea machines and ventilators due to health risks from soundproofing foam breaking down, and the company recently halted sales of the devices in the U.S. Problems with inaccurate readings from pulse oximeters have also garnered scrutiny, with some agency advisors calling for faulty products to be recalled.
The pace of innovation in 2024 is expected to exceed 2020 to 2022 levels, with cardiovascular, digital-health-device, and neuromodulation segments gaining momentum, observes a recent McKinsey study. Advanced imaging, microelectronics, miniaturization, and new treatment modalities, such as renal denervation, are spurring innovation in underserved disease areas. These exciting advances can fuel the next wave of growth and improvements in patients’ quality of life. The pace of innovation also means more competition for MedTech companies. Increasingly, it’s the big, novel innovations that will drive commercial relevance and growth—incrementalism won’t be enough.
Performance across geographies will continue to be lumpy. In 2024, McKinsey projects that China, Japan, and the United States will contribute two-thirds of near-term industry growth in MedTech. Across more established markets, such as Japan and the United States, growth continues to be driven by innovation and the adoption of innovative technologies. In the United States, commercial execution and innovation will be the hallmarks of growth.
The market in Japan will likely behave similarly, though CFOs and finance leaders there will need to be thoughtful about managing currency risk (for example, through hedging strategies). Domestic and international companies are facing foreign exchange challenges in Japan, making the US market even more critical to overall industry growth.
Growth in Europe will likely slow after a year in which price increases saw a step-up in the underlying growth rate. MedTech companies that thrive in the European market will tap fresh solutions to help providers manage workforce shortages and improve health economics through reduced readmissions and shorter hospital stays.
Elsewhere, MedTech leaders are tackling difficult strategic choices. China has delivered tremendous growth over the past decade. However, increasing complexity, local competition, and volume-based procurement have posed challenges for multinational corporations. India will begin to make a bigger splash, thanks to favorable governmental-policy changes, increased investment flow, a maturing tech ecosystem, and the emergence of growing local businesses that are increasing provider access to technology and training.
Leaders in AI adoption will start to see the benefits of scale. The underlying technologies of generative AI (gen AI)—namely, foundational models—have a long history in life sciences and MedTech. Foundational models representing complex structures have already been used in many insight-generating tasks, particularly in product development. For example, digital-twin technologies (virtual representations of physical MedTech devices paired with deep-learning models) have been used to validate alternative, and more effective, device designs. Most of the gen-AI-related activity in MedTech to date has focused on device enablement, functionality, and R&D, with untapped opportunities in commercial, supply chain, and other business functions.
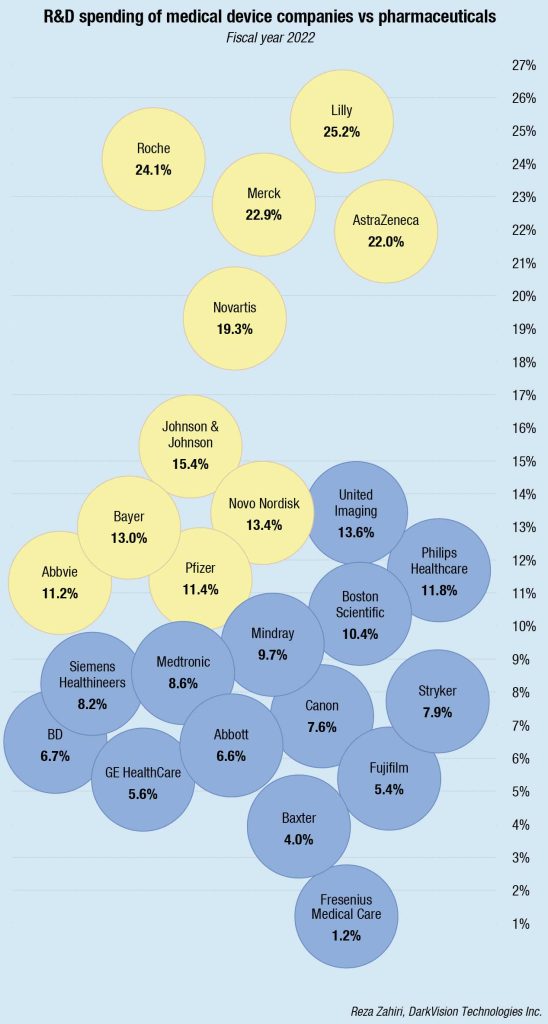
MedTech companies that adopt gen AI are starting to gain productivity benefits, starting with low-hanging fruit such as copilots for workers in HR, IT, finance, and legal roles. Companies are beginning to explore the impact of gen AI on commercial and operational roles. Because of regulatory requirements, the deep integration of AI in medical products and services remains years away. However, some companies will start integrating gen AI into their products and software, such as by leveraging voice prompts. New capabilities and talent will be needed to capture the business value fully. Given the rapid pace of innovation, early adopters are likely to have an advantage over the competition.
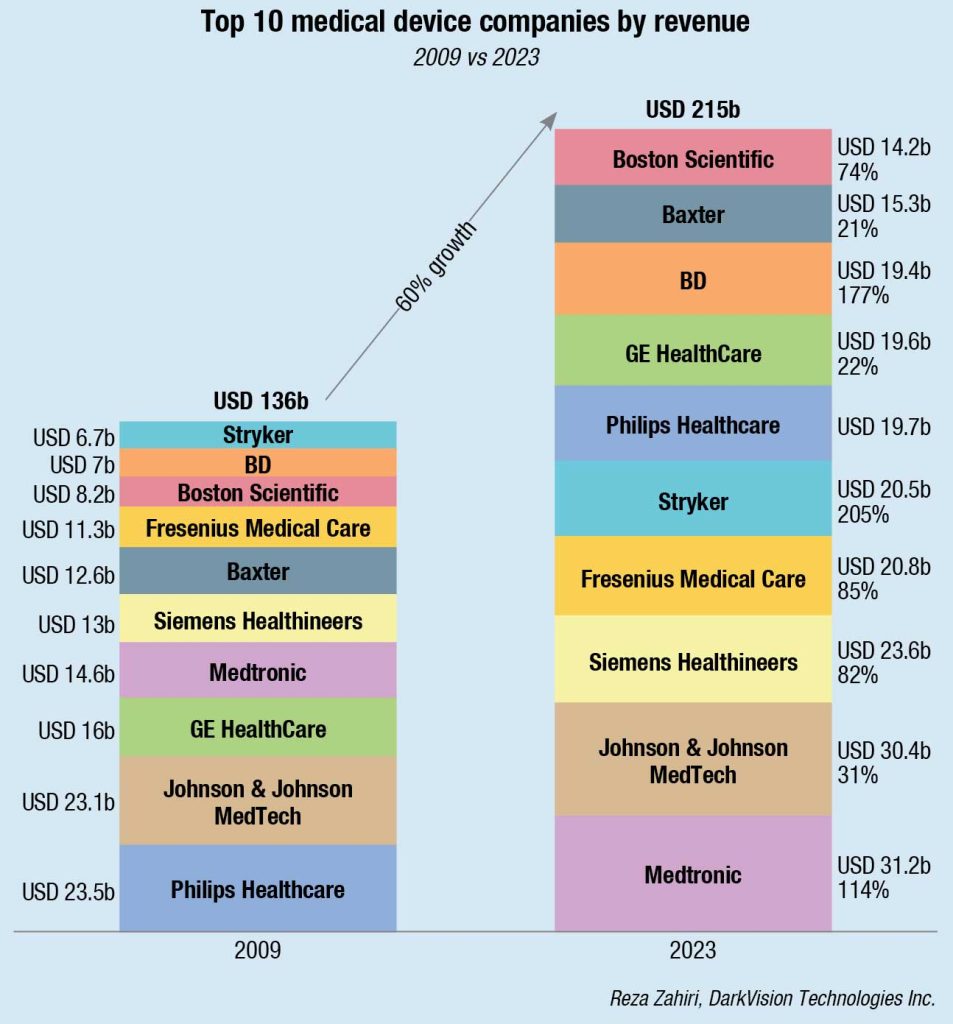
M&A deal volumes will likely remain stable, with a continued balance of growth and at-scale transactions. MedTech M&A slowed in 2023 amid earnings challenges, macroeconomic uncertainty, and rising interest rates. Meanwhile, large buyers set a precedent of paying premiums at or above 52-week highs. Many of these buyers were in pursuit of meeting rising growth expectations and unlocking margin expansion.
While growth-focused tuck-in deals will remain critical to value creation, they are not always available to companies at attractive valuations. Another tool that companies are increasingly exploring is at-scale transactions. Larger acquisitions can offer operating leverage, which can help MedTech companies improve margins that currently sit near 2018 levels; they can also help companies in lower-growth markets improve their commercial presence with more end-to-end solutions that help care teams streamline operations and focus on patient care.
| Top 5 M&A deals by value in the medical devices industry 2022 |
||||
| Target | Acquirer | Deal value | Date announced | Deal type |
| Abiomed | Johnson & Johnson | USD 16600m | Nov, 2022 | Acquisition |
| Summit Health | VillageMD | USD 8900m | Nov, 2022 | Acquisition |
| Signify Health | CVS Health | USD 8000m | Sep, 2022 | Acquisition |
| 1Life Healthcare | Amazon | USD 3900m | Jul, 2022 | Acquisition |
| Globus Medical & NuVasive | USD 3752m | Feb, 2023 | Merger | |
| GlobalData Medical Devices Intelligence Center | ||||
The volume of M&A activity is anticipated to remain low but the deals that are executed will show more balance across deal sizes. MedTech companies continue to have “dry powder” that accumulated during the Covid-19 pandemic, with approximately USD 55 billion of cash and cash equivalents. However, high-growth, at-scale, and profitable targets remain scarce. Interested acquirers will need to act quickly, given the scarcity of options.
Although obstacles remain, the MedTech industry is poised to continue to deliver benefits to all its stakeholders, concludes the McKinsey report.
M&A in Q4 2023.
In the global medical devices industry, there were 130 M&A deals announced in Q4 2023, worth a total value of USD 9.4bn, according to GlobalData’s Deals Database. The USD 3.1bn acquisition of Olink Holding by Orion Acquisition was the industry’s largest disclosed deal.
In value terms, M&A activity increased by 124 percent in Q4 2023 compared with the previous quarter’s total of USD 4.2bn and fell by 73 percent as compared to Q4 2022. Related deal volume increased by 18 percent in Q4 2023 versus the previous quarter and was 10 percent lower than in Q4 2022.
Notably, foreign direct investments related deals accounted for a 32 percent share of the global medical devices industry’s M&A activity in Q4 2023, up 2 percent over the previous quarter.
Bringing innovation to life
As MedTech continues to evolve, treatments are becoming more personalized. Physicians are more regularly reviewing data remotely and offering recommendations for treatments and even helpful home products. For example, an adjustable bed is now on the market that can sense when someone is snoring, and the bed automatically changes its incline to try and help reposition the person to open their airways. This may be a key solution for those who struggle with sleep apnea.
From wearables to AI-powered innovation, medical technology has opened the door to more personalized and real-time care. modern healthcare products getting smarter and more efficient? A key aspect of this evolution is the involvement of wearable sensors, edge computing, and wireless devices to create seamless connection points useful for the entire medical ecosystem of doctors, nurses, engineers, designers, sourcing professionals, patients, families, and others.
Semiconductor suppliers are providing the path for real-time diagnosis and personalized treatment. Their products integrate functions, including how to process information at the far edge, along with security, computing, and connectivity measures.
The impact of IoT will continue to grow as more medical sensors are developed and drive more secure connections to deliver sensitive health data. As device usage keeps increasing among the general population, there will be more data to store and make sense of, which will spur additional AI models doing the detection work that doctors and specialists are currently charged with today. Using devices for continuous monitoring is already showing the deep and remarkable impact personalized healthcare can make.
While the MedTech industry continues to face significant challenges related to regulatory requirements, cybersecurity issues, recalls and lawsuits, leaders in the industry are navigating and overcoming these areas to push innovation forward like never before.
The MedTech industry stands as a beacon of innovation, heralding a healthcare revolution that promises to transform patient outcomes and delivery systems alike. As the sector grapples with regulatory hurdles and cybersecurity concerns, the future remains bright, fuelled by technological advancements like AI, telemedicine, and robotic surgery. These innovations pave the way for more personalized, efficient, and accessible healthcare, positioning MedTech as a pivotal player in shaping a healthier, more resilient society.













