MB Stories
ECG – Redefining standards in cardiac care
The ECG market has witnessed substantial progress and broadened its horizons in recent years, highlighting the sector’s robust expansion and promising future prospects.
In the realm of cardiology, the electrocardiogram (ECG) stands as a cornerstone diagnostic tool, offering invaluable insights into heart health. Over the years, ECG technology has undergone significant advances, revolutionizing cardiovascular care.
Traditionally utilized by both cardiologists and non-cardiologists alike, ECG monitoring provides a comprehensive view of the heart’s structural and physiological condition. Through the recording of electrical impulses generated by the heart muscle, ECG machines produce detailed electrocardiograms, showcasing the timing and strength of these signals. These waveforms serve as critical indicators of abnormalities, such as irregular heart rhythms, conduction disorders, or ischemic episodes.
In recent times, the ECG industry has witnessed a remarkable shift toward smaller, more compact, and mobile monitoring systems. This transition has been marked by the emergence of wearable ECG devices, facilitating wireless transmission of data through small adhesive patches. Integration with smartphones has further streamlined the monitoring process, allowing for seamless data collection and analysis.
A significant leap forward has been the integration of AI into ECG analysis. This innovation empowers clinicians with faster and more accurate diagnostic capabilities, enhancing patient care and outcomes.
These advancements in ECG technology and signal processing signify a new era in cardiac care. From wearable devices to AI-driven analysis, these innovations empower individuals to take proactive steps toward managing their cardiovascular health and leading healthier lives.
Indian market dynamics
The Indian ECG equipment market in 2023 is estimated at ₹290 crore at 26,600 units.
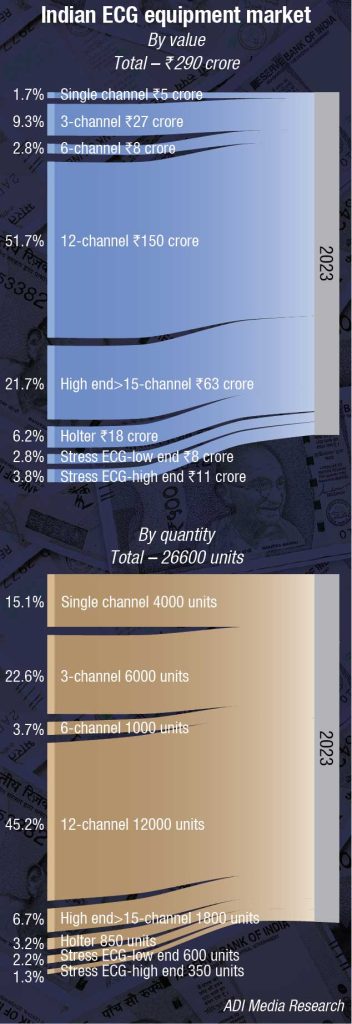
The single-channel ECG machine is used primarily by the pharma companies. In the hospitals, they are used when received as a gift; buying is no longer prevalent for this segment. The price conscious buyer is going in for a 3-channel unit, albeit it is on its way out. The volume in 2023 over 2022 has almost halved. The 6-channel machines have lost relevance since they are sold at almost similar price points as the 12-channel machines. It is the 12-channel machines that are dominating the market.
|
Leading players-Indian ECG equipment market |
|
| Tier 1 | BPL and GE |
| Tier 2 | Schiller and Philips |
| Tier 3 | Mindray, Nihon Kohden, and Comen |
| Tier 4 | Allied, Skanray, Allengers, Nidek, Bionet, Mortara, Contec, Edan, and RMS |
| Others | Nasan, Medikit, Forest, Silverline Meditech, Omron and regional brands |
|
*Vendors are placed in different tiers on the basis of their sales contribution to the overall revenues of the Indian ECG equipment market. ADI Media Research |
|
The discerning customer opts for the high-end machines that are 15-, 18-, or 22-channels. The use of this contributes to a faster and more accurate diagnosis of STEMI, particularly in the emergency department, facilitating the prompt reperfusion therapy. In up to 30 percent of patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS), the initial 12-lead ECG may be normal or showing non-specific abnormalities only. Nonetheless, a diagnostic initial ECG in a patient with AMI will allow the physician to promptly start the appropriate therapy, mainly reperfusion. It has repeatedly been demonstrated that recording additional leads on initial ECG may improve its sensitivity and the prognosis of selected cases of ACS patients. Moreover, additional lead ECGs may reveal more accurately the extent of the myocardial injury. It is known that posterior or postero-lateral AMI might not be manifested with ST elevation on the classic 12-lead ECG. If this were the case, especially in the emergency department, then these patients could be offered specific reperfusion therapy, either thrombolysis or percutaneous coronary intervention. Therefore, the recording of posterior leads (V7, V8, V9) seems to be valuable and practical. Surprisingly, less than 40 percent of physicians request the posterior leads on the initial ECG of patients hospitalized for ACS.
The Holter is found very useful for remote ECG interpretation consultancy. The services can receive and interpret ECGs – along with other information – using telephone and digital methods. The ECG is transmitted from a primary care center to the service provider. This can be done automatically from devices supplied by the services. Alternatively, ECGs may be uploaded to the internet using a software platform or webpage, or sent by email. A cardiac technician, cardiac nurse, consultant cardiologist, or specialist consultant cardiologist, such as an electrophysiologist interprets the ECG. Recordings from Holter, loop, and event monitors can be interpreted live. The signal can be continuously transmitted to allow the interpreter to monitor activity in real time. The interpreter returns a report with their ECG interpretation or recommendations to the patient’s primary care clinician within an agreed timeframe.
The stress ECG machine monitors heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, electrical activity (on an electrocardiogram) and the person’s level of tiredness. The high growth of this segment is driven by its versatility as it is widely used for assessing cardiovascular health. The familiarity of walking or running on a treadmill makes it a preferred method for inducing physical stress during a stress test. Moreover, treadmills allow for dynamic and controlled exercise, facilitating a gradual increase in speed and incline to elevate the heart rate and induce stress. There is a continuous advancement in stress ECG equipment technology, including improved ergometry features and integrated monitoring systems.
Technological advancements and emerging trends in electrocardiography
 Dr Arathy R
Dr Arathy R
Senior Design Engineer, Advanced Technologies,
Skanray Technologies
Electrocardiogram (ECG), a benchmark tool for detecting and classifying cardiovascular diseases, has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by technological innovations and a growing emphasis on remote patient monitoring, wearables, data analytics, etc., as enlisted below.
Miniaturization and portability. Advances in electronics have led to smaller, portable ECG devices with comparable accuracy to traditional machines. These portable devices enable clinicians to perform ECG analysis in various settings, such as in ambulances, remote clinics, etc.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning. Various algorithms are integrated into the ECG to improve accuracy in interpreting the results. These smart algorithms have paved a new path for accurate interpretation of results, thus aiding the clinicians in early diagnosis of diseases.
Wireless connectivity. Nowadays, most ECG machines have Bluetooth/Wi-Fi capabilities, allowing seamless data transfer to electronic health records or cloud-based platforms. This connectivity helps clinicians with remote patient monitoring to provide timely interventions.
Synthesizing ECG waveforms. Exploring methods to mathematically derive the additional ECG waveform from the standard lead configurations, such as 5 or 12 lead for more information and specialized diagnosis.
Cloud-based ECG analysis. It enables the storage and analysis of large volumes of ECG data that the clinicians can access from any location, facilitating collaborations among specialists and improving patient care.
Wearable sensors. Many consumer-grade smartwatches and fitness trackers are equipped with ECG sensors to monitor heart rate and detect irregularities. ECG adhesive patches are available that patients can wear to continuously record their heart activity.
Applications of continuous ECG recording embedded in armchairs have been studied recently, developing capacitive electrodes and conductive fabrics.
Further, the advancements in nanotechnology may lead to even smaller, more discreet wearable ECG sensors.
Integration with telemedicine platforms. The rise of telemedicine has led to integrating ECG devices with virtual healthcare platforms.
Data analytics. ECG data, when combined with other health information, can provide insights into an individual’s overall health. Various data analytics tools help in identifying trends and predicting potential heart issues.
In summary, this century-old diagnostic tool is experiencing a renaissance as novel technologies and their potential clinical utility have come to light.
Global market dynamics
The global ECG market was valued USD 8.1 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 11.3 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 6.9 percent from 2023 to 2028, according to MarketsandMarkets.
Factors, such as the rise in the number of heart specialty centers worldwide and awareness programs that help clinics and hospitals prepare patients for ECG without complications, contribute to driving the global market for ECG.
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI), wireless communication, and other advanced functionalities accelerates product development, facilitating the swift introduction of innovative solutions to the market. This, in turn, enhances patient outcomes, reduces healthcare expenditures, and spurs heightened demand for ECG testing on a global scale. The rising adoption and demand for technologically advanced ECG monitors present substantial growth prospects for participants in the global electrocardiograph market. For instance, market players are concentrating on launching state-of-the-art ECG monitors to cater to escalating demand.
The overall market for ECG devices is currently experiencing significant growth, propelled by several key factors, such as technological advancements, increased adoption of remote monitoring solutions, and heightened awareness programs promoting ECG testing. Notably, mobile cardiac telemetry (MCT), which is primarily utilized for ambulatory cardiac monitoring, plays a pivotal role in this growth trajectory. MCT devices offer real-time ECG monitoring and automatic detection of abnormalities, providing a convenient and efficient solution for patients. With its technological advantages over traditional long-term monitoring options, MCT has emerged as a transformative innovation in the medical devices industry.
However, manufacturers must prioritize software development to ensure data security and prevent potential leaks, which could result in regulatory challenges. Despite these considerations, the increasing adoption of MCT is expected to drive substantial growth in the coming years.
The market faces a significant hurdle in the form of expensive nature of instruments and maintenance. Furthermore, the lack of proficient professionals capable of operating and interpreting ECG results can hinder the effective utilization of ECG equipment. Alternative diagnostic technologies may compete with ECG devices for market share. Advancements in these alternative technologies could reduce the demand for traditional ECG equipment.
Additionally, stringent regulatory requirements or delays in obtaining necessary approvals for ECG devices can slow down product development and market entry. Compliance with complex regulations can also increase manufacturing costs and time-to-market, which is further complicating the situation.
Regional insights. North America accounts for the major ECG market with 39-percent share. This can be attributed to the rising demand for diagnostics due to the increase in the prevalence of cardiovascular disease (CVDs), coupled with the presence of skilled physicians, to conduct advanced diagnostic procedures. In addition, the increasing number of diagnostic procedures to detect CVDs in hospitals and clinics is also fuelling the adoption of diagnostic ECG.
Asia-Pacific region is projected to witness rapid growth with 5.77-percent CAGR as a result of increasing penetration of leading players in the region. In addition, the growing adoption of well-established healthcare infrastructure and CVDs is one of the factors driving the market in this region. CVDs have now become the leading cause of mortality in India. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), CVDs, such as ischemic heart disease and cerebrovascular like strokes account for 17.7 million deaths. This is due to a remarkable change in lifestyle, lack of physical activity, poor diet, and addiction to tobacco and alcohol.
Technical advancements
The dynamic growth of the ECG industry is not merely a tale of technological advancement; it is a narrative of relentless innovation shaping the future of cardiac care. Imagine a world where the rhythm of life is not just a metaphor but a tangible reality, captured and deciphered by cutting-edge devices and technologies.
Holter devices. In recent years, the field of cardiology has witnessed remarkable advancements in Holter devices, revolutionizing long-term cardiac monitoring.
This innovative Holter device represents a significant leap forward in long-term cardiac monitoring, offering features that were previously unavailable. One notable advancement is the extended duration of monitoring, enabling up to several weeks of continuous recording. This prolonged monitoring period provides healthcare professionals with a comprehensive view of a patient’s cardiac activity, allowing for more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
The latest Holter devices boast wireless connectivity, facilitating seamless data transmission, and remote monitoring, empowering healthcare providers to promptly intervene in case of any concerning developments. Additionally, wireless connectivity enhances patient comfort and convenience, as it eliminates the need for cumbersome wired connections.
Furthermore, they incorporate advanced algorithms and analytic tools to enhance data interpretation. These algorithms can detect subtle abnormalities in cardiac rhythms, allowing for early detection of arrhythmias and other cardiac conditions. Such early detection is crucial for preventing complications and improving patient outcomes.
Over the next decade, the Holter monitors segment is projected to experience a significant growth. This surge is driven by rising demand for detecting cardiac arrhythmias and diagnosing patients with such conditions. Holter monitors are increasingly utilized not only for detecting arrhythmias but also for quantifying them, evaluating antiarrhythmic therapy, and analyzing prognostic aspects.
Integration graphical software tool. In a recent development, a free software tool named ECGDT has been introduced, offering a comprehensive approach to ECG analysis and diagnosis.
ECGDT boasts several functionalities crucial for cardiac diagnosis. Firstly, it facilitates the detection of beats present on the ECG, operating at both single and multi-channel levels. Moreover, it excels in identifying beat waves and diagnosing various cardiac abnormalities. Notably, ECGDT demonstrated a remarkable capability to detect 100 percent of several cardiac abnormalities, including bradycardia and tachycardia.
Evolution of electrocardiogram (ECG) solutions – Shaping future cardiac care
 Aditya Kohli
Aditya Kohli
CFO & Director,
Allied Medical Limited
Electrocardiogram (ECG) technology has undergone remarkable advancements in recent years, revolutionizing cardiac diagnostics and patient care. From traditional resting ECGs to portable monitoring devices and cloud-based solutions, the landscape of ECG technology is continually evolving to meet the demands of modern healthcare. With advancements in mobility, ease of use, and interoperability, ECG solutions are transforming the way cardiac data is collected, interpreted, and managed. Allied Medical Limited (AML) stands at the forefront of this transformation, providing innovative medical technologies and services that are reshaping patient care worldwide.
Over the past decade, there has been a noticeable shift toward smaller, more compact, and mobile ECG monitoring systems. These systems not only offer greater mobility but also streamline workflow and improve connectivity with electronic medical records (EMRs). A key feature of modern ECG solutions is the inclusion of interpretation algorithms, providing clinicians with a virtual second opinion based on gender- and age-specific criteria. This enhances diagnostic accuracy and aids in clinical decision-making.
Modern ECG machines are designed with simplified operation in mind, featuring touch-screen interfaces, alphanumeric keypads, and seamless connectivity with ECG management systems, Health Level Seven (HL7) standards, hospital information systems (HIS), and EMRs. Integration with hospital systems is becoming increasingly vital, enabling paperless healthcare and facilitating the seamless flow of patient data between departments, hospitals, and referring physicians.
The evolution of ECG solutions represents a significant milestone in cardiac diagnostics, ushering in an era of enhanced mobility, connectivity, and diagnostic accuracy. Allied Medical Limited continues to lead the way in delivering transformative medical technologies and services, empowering clinicians to predict, diagnose, and manage cardiac diseases more effectively.
The rapid pace of technological advancements in ECG technology is reshaping the landscape of cardiac diagnostics and patient care. From miniaturized portable devices to AI-powered interpretation algorithms and cloud-based solutions, ECG technology continues to evolve, offering new opportunities for early detection, remote monitoring, and personalized treatment. As these emerging trends continue to unfold, the future of ECG technology holds immense promise for improving cardiovascular health outcomes and enhancing the quality of care for patients worldwide.
Furthermore, the tool’s graphical software interface (GUI) received commendable feedback, with all usability estimators scoring values within the positive range, signifying its efficiency and user-friendly design. ECGDT emerges as a valuable aid in the diagnosis of diverse medical abnormalities, supported by its robust diagnostic capabilities and intuitive interface.
However, despite the advancements, challenges persist in the widespread adoption of computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems in healthcare. Concerns regarding complex interfaces and the need for user trust remain prevalent among some users. Additionally, limitations in detecting certain conditions, such as Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome, underscore the importance of expanding research efforts and datasets to enhance diagnostic accuracy.
Looking ahead, future endeavors aim to address these challenges and further refine ECGDT. Improvements in detection results, interface enhancements, and the addition of new diagnostic capabilities for a broader range of cardiac conditions are on the agenda.
OWSK. A novel model for arrhythmia detection based on a cascading technique that utilizes a combination of the one-sided selection (OSS) method, support vector machine (SVM), and k-nearest neighbor (KNN) algorithms, this model is denoted by (OWSK) model to classify four types of electrocardiogram (ECG) heartbeats following inter-patient scheme.
The OWSK model consists of three stages. In the first stage, the OSS method is used to address data imbalance and reduce noise by selectively choosing relevant samples and removing noisy, borderline, and redundant ones. The second stage involves extracting the most relevant frequency domain features using wavelet transformation (WT) and power spectral density (PSD) techniques. The third stage employs a cascading process where a classifier is constructed from SVM trained on the entire dataset to classify normal and abnormal beats. Subsequently, KNN is trained specifically on the three irregular minority classes to classify the three types of arrhythmias – ventricular ectopic beats, supraventricular ectopic beats, and fusion beats (V, S, and F).
The performance of the OWSK model was evaluated using various metrics, including accuracy, recall, precision, and F1 score. The results showed the superiority of the proposed model in medical diagnosis compared to latest works.
This model presents a robust and effective model for accurately detecting various types of arrhythmias in ECG data, showcasing its potential for enhancing medical diagnosis and patient care.
Integration of AI. The integration of AI in ECG analysis marks a quiet yet transformative revolution in cardiovascular care. Over the past few years, FDA-approved AI algorithms have emerged, focusing on interpreting ECGs to diagnose arrhythmias and, more recently, structural and ischemic diseases. This burgeoning landscape has seen collaboration among academia, health systems, life science companies, and major MedTech players, ushering in a new era of innovation.
While regulatory and reimbursement frameworks are still evolving, the potential of AI in ECG analysis to revolutionize diagnosis and patient management is undeniable. With the promise of quicker, more accurate diagnoses, particularly in ambulatory care settings, and the emergence of algorithms for detecting a wider range of cardiovascular conditions, the integration of AI in ECG analysis holds immense promise for improving patient outcomes and reshaping the future of cardiovascular care.
Cutting-edge research
Research is continuous, where scientific inquiry unveils ground-breaking advancements poised to reshape the landscape of cardiac care.
MiniECG. A team of researchers, including cardiovascular medicine specialists as cardiologists, technologists, and clinicians, have collaborated to develop the miniECG device. Unlike many single-lead portable ECG devices primarily designed for rhythm disorders, the miniECG is a smartphone-sized portable device with four dry electrodes. It is capable of recording high-quality multi-lead ECGs by simply placing the device on the chest.
The study aimed to assess the miniECG’s performance in detecting ST-segment deviations indicative of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in patients presenting with chest pain in the emergency department (ED). Results showed that the miniECG achieved a sensitivity of 65 percent in detecting ST deviations in patients with occluded myocardial infarction (OMI), along with a specificity of 92 percent and a low rate of false positives.
The findings suggest that the miniECG holds promise in reducing time to treatment by enabling rapid identification of patients requiring urgent evaluation and transport to a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) center. Unlike other single-lead ECG wearables, the miniECG demonstrated the capability to detect ST deviations for various culprit vessels.
However, challenges, such as false positives and limitations in sensitivity compared to 12-lead ECGs, particularly in detecting occlusions involving the right coronary artery (RCA), were noted. Further research is necessary to refine device placement and address these limitations. Additionally, there is potential for the miniECG in home-based monitoring pending further validation and integration of AI.
Early detection of three heart diseases using ECG-AI. Researchers and clinicians at Mayo Clinic are leveraging AI technology to enhance the diagnostic capabilities of ECGs, a cornerstone in cardiovascular assessment for over a century. By employing AI-enabled ECG analysis, their aim is to detect heart conditions earlier, thereby potentially improving patient outcomes and longevity. Researchers have developed ECG-AI algorithms to predict various heart conditions, including atrial fibrillation, amyloidosis, aortic stenosis, low ejection fraction, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), among others. These algorithms utilize both traditional 12-lead and single-lead ECG data obtained from smart watches and portable devices.
One notable application of ECG-AI is in the detection of low ejection fraction, a condition where the heart pumps less blood than normal. The AI algorithms for detecting this condition have received clearance from the FDA and are poised for commercial development by licensed entities.
Furthermore, AI-assisted ECG analysis shows promise in diagnosing peripartum cardiomyopathy in pregnant or postpartum women, as well as detecting early stages of cardiac amyloidosis. This technology is particularly valuable in underserved populations where access to comprehensive healthcare is limited.
While ECG-AI offers significant potential for early detection of heart conditions like HCM, further research and clinical validation are needed to ensure its practicality, accuracy, and accessibility. However, once fully developed and validated, AI-enabled ECG analysis could revolutionize heart health checkups, enabling early detection and intervention, especially in high-risk populations like athletes and individuals with a family history of heart disease.
ECGI vest. Another ground-breaking study led by researchers at University College London (UCL) introduces a novel electrocardiographic imaging (ECGI) vest, designed to meticulously map the heart’s electrical activity, potentially revolutionizing the identification of individuals at high risk of sudden cardiac death.
The research, published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, addresses the longstanding challenge of detailed electrical mapping, historically reliant on invasive procedures or cumbersome single-use devices.
The ECGI vest, developed with funding from the British Heart Foundation (BHF) and the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, offers a reusable and time-efficient solution, requiring only five minutes per patient. Featuring 256 sensors, the vest captures electrical data that, when combined with MRI images, generates 3D digital models of the heart and its electrical waves. Dr Gaby Captur and Dr Matthew Webber, co-developers of the vest, highlight its potential as a screening tool for life-threatening heart rhythms, as well as its utility in assessing treatment impacts. While the vest’s reliability and durability have been demonstrated in feasibility studies involving 77 patients and subsequent successful use in 800 patients, its commercialization and widespread availability are still under exploration, with patents secured and manufacturing partnerships being pursued. This research heralds a promising advancement in cardiac risk assessment, with implications for personalized treatment strategies and improved patient outcomes.
Some challenges
Despite improvements, hospitals are still grappling with acute heart attacks post Covid-19, particularly in maintaining optimal door-to-balloon (D2B) times. D2B time, which measures the interval between a heart attack patient’s arrival at the hospital and the initiation of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), faced significant challenges during the pandemic.
Factors, such as Covid-19 screening requirements, isolation protocols, and enhanced cleaning procedures in cardiac catheterization labs led to delays in D2B times, making it difficult to meet the crucial 90-minute benchmark for optimal outcomes. Shortages of healthcare and EMS workers further exacerbated the issue, causing delays in emergency response and treatment initiation.
To address these challenges, hospitals implemented proactive measures, such as multidisciplinary team re-education, additional staff involvement, and collaboration with emergency medical services to minimize transport delays.
Furthermore, processes like pre-activating all field STEMIs and conducting regular drills were instituted to streamline patient care pathways and optimize time management. Despite initial setbacks, these efforts yielded tangible improvements, with facilities successfully reducing their D2B times from 73 minutes to 60 minutes.
Outlook
As the ECG industry continues to thrive on the fuel of innovation, driven by technological advancements and ground-breaking research, the future of cardiac care appears promising and transformative. With ongoing advancements, cardiac health is poised to become more attainable for individuals worldwide.
The journey toward improved patient outcomes and enhanced diagnostic capabilities is an ongoing one, marked by challenges like post Covid-19 disruptions in cardiac care pathways. However, proactive measures and collaborative efforts within the healthcare community are paving the way for overcoming these obstacles and ushering in a future where cardiovascular diseases can be detected earlier, managed more effectively, and ultimately, prevented with greater precision.
As we look ahead, the horizon appears bright with possibilities, promising a future where heart health is not just a goal but a tangible reality for individuals worldwide.
Second Opinion:-
Advancing patient care – A doctor’s view on modern ECG machines.












