Industry
Continuing the automation revolution

The need for automation and the benefits derived from it will only be clearer in the future, as experiments become more complex, workflows faster, and researchers more accustomed to mapping out pathways of experiments from their desks, with much less physical involvement.
Every minute, a massive amount of healthcare data is generated and extracted for useful information. The healthcare industry currently generates approximately 30 percent of the world’s data volume. Moreover, the healthcare data is expected to grow at a rate of more than 30 percent per year until 2025. As a result, a massive volume of data necessitates an automated system to process crucial healthcare data, increasing the demand for lab automation. The rapid spread of coronavirus worldwide has also led to millions of swab testings in private and public labs, which again increased the volume of patient data. To curb the spread of the Covid-19 pandemic, companies shifted their focus toward automation, and are taking the help of robotic lab systems for testing and processing results.
The rise in advantages offered by lab automation is one of the major factors anticipated to boost market growth in the near future. For clinical laboratories, a paradigm shift from complete manual intervention to lab automation possesses several advantages. Some major advantages include increased productivity, reliable results, safe working conditions, and immense savings on time, space, and cost of tests. Lab automation facilitates the usage of laboratory equipment for monotonous tasks, such as labeling tubes and sample verifications, and also helps in reducing and minimizing the physical strain that is caused by manual tasks, reducing costs incurred and saving lab space. Thus, various advantages offered by the automated systems are expected to encourage small and large laboratories to adopt these workstations in coming years.
Future-proofing your lab with next-generation automation
 Sridhar Natarajan
Sridhar Natarajan
Managing Director – South West Asia,
Beckman Coulter Diagnostics
Laboratories are living through unprecedented times, with a sharp increase in testing and the need to create greater workflow efficiencies. Space constraints and business demands are at the heart of what is driving laboratories to upgrade their automation systems. According to a report, published by IMARC Group in May 2022, the India laboratory automation market is expected to reach USD 135.21 million by 2027, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.49 percent during the forecast period (2022–2027)1.
Need for automation. Laboratory testing is widely relied upon when it comes to making a diagnosis. With staffing shortages, increased testing volumes, and the need to improve turnaround time, labs are faced with the challenge of reducing errors. Estimates find that 70 percent of all healthcare decisions affecting diagnosis or treatment involve laboratory testing2. When critical lab results are the basis of clinical decisions, reducing errors, when it comes to the pre- and post-analytical phase of lab testing, is of paramount importance.
Automation for all. Automation is key when it comes to minimizing time-consuming errors, and is a necessity for any lab striving to meet the ever-evolving demands of today. Not only does automation take over important tasks from over-worked personnel but it also standardizes processes, consolidates diagnostic areas within the same workspace, and reduces manual steps. In addition, automation can mitigate bottlenecks that occur during sample preparation by processing samples quicker and more efficiently with less variation than humans. This allows labs to benefit from increased accuracy and repeatability throughout the total testing process. A good automation system allows labs to keep their focus where it belongs – advancing patient care.
Designing automation for your laboratory. At Beckman Coulter, we believe that labs of all sizes should be able to leverage the benefits of automation to address their challenges. Our automation portfolio offers a solution that fits every lab’s space constraints. As your laboratory partner, we can help you transform your lab by improving workflow efficiency across all disciplines – hematology, chemistry, immunoassay, and clinical informatics. Regardless of the size of your lab, our diagnostic products and solutions can help you deliver greater insights, and accelerate patient care.
References
-
India Laboratory Automation Market: Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2022-2027 https://www.imarcgroup.com/india-laboratory-automation-market-report
-
Badrick T. (2013) Evidence-Based Laboratory Medicine. Clin Biochem Rev. 2013 Aug; 34(2): 43–46
Increase in demand for miniaturization is another factor expected to impact the market growth significantly in the near future. One of the major causes for the implementation of automated systems and workstations at clinical laboratories is to facilitate miniaturization of research processes in order to develop solutions for various complex lab automation tasks for applications, such as biotechnology, microbiology, and clinical chemistry, among others.
Furthermore, miniaturization of these processes facilitates easy expansion, monitoring, and cultivation of cells increasing turn-around times for point-of-care (POC) settings.
Growth in the number of applications of lab automation is expected to fuel market growth over the next 5 years. In the recent past lab, automation has found several applications that have revolutionized laboratory processes that were conventionally carried out by manual intervention. Some of these include applications, such as automated chemistry applications, synthetic biology, cell line development, genomics, cellular assays, and drug discovery, among others. Therefore, an increase in the number of clinical applications of automated instruments for labs is anticipated to increase the adoption of lab automation in coming years.
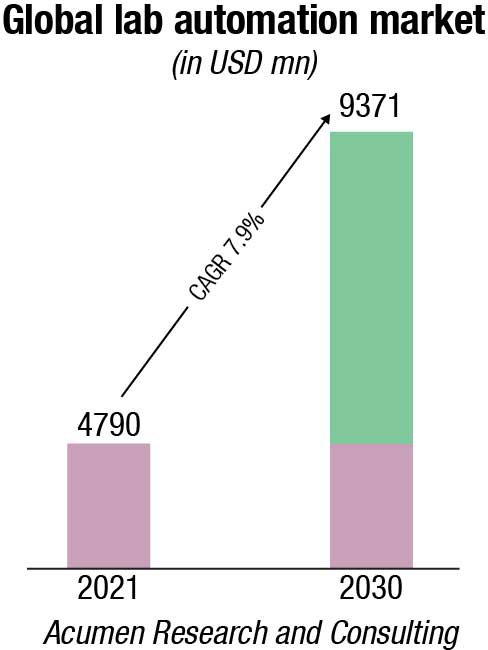
The global lab automation market accounted for USD 4790 million in 2021, and is estimated to reach USD 9371 million by 2030, with a significant CAGR of 7.9 percent from 2022 to 2030. The rise in the number of laboratory tests globally, increasing standardization of workflows in laboratories, and surging research and development investments in pharma and biotechnology industries are the prominent factors that are driving the growth of the global lab automation market. To fulfill the expanding needs of the healthcare sector, pharmaceutical and biotechnology businesses are investing heavily in research.
However, the sluggish demand in the small and medium laboratories could hamper the market from growing. The initial cost as well as the maintenance cost of lab automation is very high for small and medium laboratories. Thus, it could be witnessed that the market has not yet matured in emerging economies.
Furthermore, growth in pharma and biotechnology industries, and improving healthcare infrastructure in developing countries, such as China and India are the aspects that are likely to fuel the market demand in the coming years. In addition to that, the integration of artificial intelligence and analytical tools in laboratory workflows is one of the lab automation trends that are generating several growth opportunities for the market during 2022 to 2030.
Companies are resuming operations and adapting to the new normal as they recover from the Covid-19 impact, which had previously resulted in preventive containment measures, such as remote working, social distancing, and the shutting down of commercial activities, all of which formed operational threats. Furthermore, the pandemic has resulted in decreased revenues and margins for hospitals and health systems, as well as decreased expenditures in automation and technology.
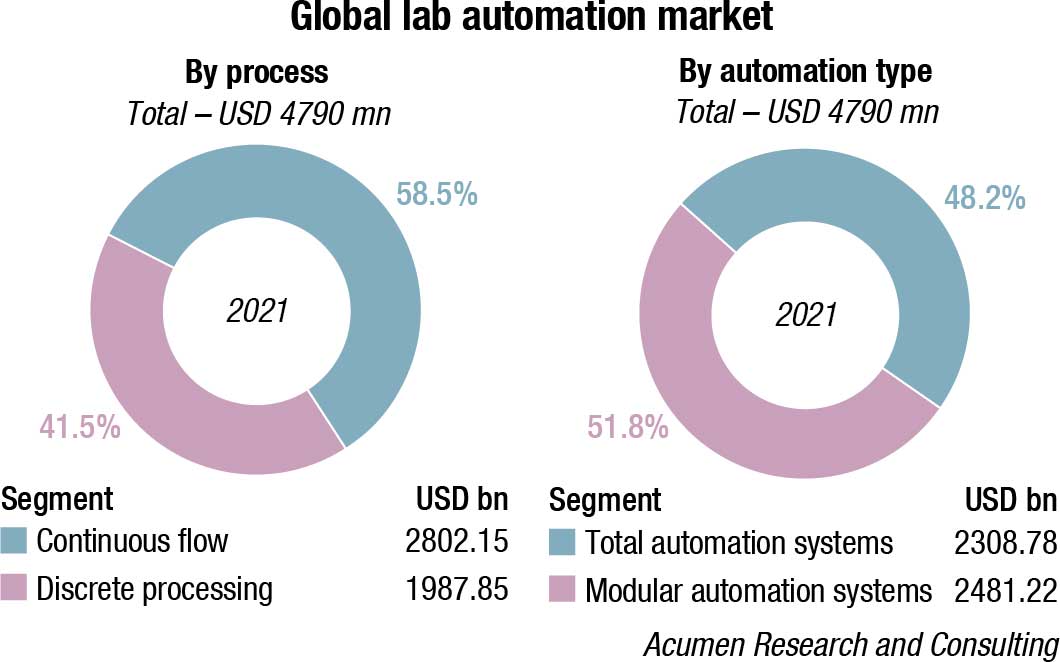
The continuous flow segment dominated the overall market, and accounted for the largest revenue share of 58.5 percent in 2021, owing to the high adoption of continuous flow in laboratories for providing high-quality services. In addition, continuous flow analysis is one of the well-established techniques and is also ideal when there is a need to analyze a higher number of samples for a smaller number of chemistries. Based on process, the market is segmented into continuous flow and discrete processing.
The discrete processing segment is anticipated to grow at a significant rate during 2022 to 2030. This can be attributed to several advantages of discrete processing over continuous flow, which is anticipated to support its adoption over the next eight years. In discrete processing, every sample is provided a discrete space, therefore, enhancing the analysis samples in this process. Thus, there is no wastage of excess reagents used for flow, as compared to continuous flow processing. This segment is anticipated to witness significant growth with its several advantages over continuous processing.
The total automation systems segment dominated the market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 48.2 percent in 2021, owing to various benefits offered by these systems. The developments in this field in various life science processes have been among the important driving factors anticipated to fuel the segment growth in the near future. Based on automation type, the market is segmented into total automation systems and modular automation systems.
Total automation systems are further segmented into steps for further process. The segment is mostly driven by the need to enable repetitive processes or technically challenging, many of the drug discovery laboratories are now adopting lab automation systems, such as benchtop automation systems.
Modular automation systems are segmented into steps involved in the further process. One of the major factors contributing to market growth is the change in consumer demand, facilitating rising uptake of modular automation systems. These systems are mostly used in fine chemical, pharmaceuticals, and food processing fields.
The clinical chemistry analysis segment dominated the market and held the largest revenue share of 27 percent in 2021. This high share is attributed to technological advancements, an increase in automated systems provided by market players, and growth in the usage of automated systems owing to their benefits, such as the reduced risk of contamination and elimination of human error, among other benefits. Based on end-use, the market is segmented into clinical chemistry analysis, photometry and fluorometry, immunoassay analysis, and electrolyte analysis, and others.
The automation of immunoassays has been witnessing significant technological advancements. With automated and hands-free processing of various small batches of immunoassays in research labs, the potential end-user has several choices for immunoassay analysis. The other end-use segment includes the use of automated systems by forensic labs and biobanks.
North America dominated the lab automation market and accounted for the largest revenue share of 37.4 percent in 2021 and is expected to maintain the position during 2022 to 2030. The growth is attributed to the presence of a well-established healthcare infrastructure, which has led to an increase in the adoption of lab automation systems in the region.
Clinical laboratories are constantly striving to improve their services by reducing turnaround times and increasing the quality of their results. Total lab automation (TLA) assists labs in meeting these challenges by providing consistency, comprehensive quality control, and fewer manual steps, all of which contribute to significantly improved laboratory performance. TLA systems are most commonly used in clinical chemistry and hematology laboratories, with clinical microbiology becoming more common.
Task-targeted automation (TTA) drew the attention of the laboratory world looking for ways to boost productivity. Laboratory managers are well aware of the need to cut costs, and they are beginning to realize that reallocating staff will have a greater impact on their bottom line than cutting reagent costs by a few pennies per test. TTA is expected to provide reduced turnaround time, reduced biohazard exposure, improved staff utilization, improved sample tracking, efficient archiving, and improved job satisfaction, all of which will lead to better patient care. This in turn is expected to drive the growth of the lab automation market.
Pharmacies can now save money on hiring and training staff while also reducing manual errors in the workplace, thanks to automation. Whether it is labeling, dispensing medication, or performing any other daily task, automated systems are more regulated and effective than humans. This factor is expected to boost the lab automation market.
As instruments have become more automated, researchers are spending less time in the lab; an individual can set up an experiment and then go home to remotely initiate and run it. This remarkable level of automation frees up time for other things. Having a machine do the bulk of the work, especially for workflows that are highly complex, allows researchers to put more emphasis on thinking and designing future experiments, and less on logistics.
Not surprisingly, the most intricate processes benefit the most from automation and miniaturization. Genomics work can be incredibly time-consuming, and often difficult to do manually. With advanced instruments, cloning methods can be reduced from the microliter to the nanoliter scale, which again saves time, materials and reagents, and money. The same is true for polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which is used in Covid-19 research and diagnostics, among others.
Synthetic biology has some of the most complex workflows, and stands to gain the most from advanced automation. With instruments that automate and miniaturize, the assembly of large DNA molecules in a synthetic biology workflow moves from 12 hours to three hours. In DNA sequencing, pooling together DNA fragments from sample libraries also becomes much faster – transferring each sample takes less than a second, using automation, which can reduce the total time from six hours to 12 minutes.
Automation is advancing along many other exciting avenues as well. Robotic transfer of plates and other materials can occur not just within an instrument, but between instruments too. This level of choreography will allow even more complex research to be carried out, with researchers monitoring larger experiments from afar. And in this age of remote working, the ability to carry out lab work from home may be especially desirable.
Remote laboratories are popping up all over the world; they allow a researcher to choose compounds online and map out an experiment remotely. The research can then be carried out at a lab anywhere across the globe, with the researcher never setting foot in a physical lab.
The central feature of moving toward more comprehensive automation is that it will silently handle unprecedented levels of complexity, both during and in preparation for experiments. For instance, machine learning systems can gain knowledge of how various combinations of reagents perform, predict and propose what might work better, see if the reagents are available and even order them, and schedule the synthesis and testing of the new compounds. Researchers are reporting doing more experiments on faster timelines with automation. This again shifts focus from doing and logistics to thinking and designing larger investigations.
An interesting example of the growing confidence in lab automation is Amazon, a company that has long embraced automation for its own business operations – most people have probably seen footage of robots shuffling items back and forth across the warehouse. Amazon has invested heavily in accumulating and optimizing its army of warehouse robots to be smaller, faster, stronger, and smarter.
More recently, the company invested in automated lab instruments in both the US and the UK to carry out regular Covid-19 PCR tests for its employees. Although it was a large financial investment, doing the testing in-house will end up saving money in the long run – and underscores the company’s commitment to automation, particularly as it moves deeper into its own public healthcare offerings.
For some organizations, the greatest barrier to automation may indeed be cost, particularly as it may seem cheaper to have a graduate student carry out an experiment than an advanced machine. The miniaturization factor implicit in automation goes a long way in reducing costs for materials, reagents, and other consumables, in addition to the sheer speed of automation.
The reality is that a lot of questions simply cannot be answered in laboratories without automation – this will increasingly cause a divide between those who have taken the plunge and those who have not. The need for automation and the benefits derived from it will only be clearer in the future, as experiments become more complex, workflows faster, and researchers more accustomed to mapping out pathways of experiments from their desks, with much less physical involvement.
The bottom line is that automation allows for more efficient and accurate research – it has already had a very real effect on the speed of developing and bringing life-saving therapies and vaccines to patients, and it will only accelerate in the coming years.












